Himachal Pradesh Economic Survey 2019-20 Chapter 11, 12, 13
(Himachal Pradesh Economic Survey 2019-20)
CHAPTER 11: Power
- The State carries immense potential for hydropower generation as it is well known as country’s hydro power hub. Hydro power development is the key engine to the economic growth of the State of Himachal Pradesh.
- The State of Himachal Pradesh has an estimated Hydro Potential of 27,436 MW out of which 24,000 MW has been assessed as harness able while the Government of Himachal Pradesh has decided to forgo balance potential in lieu of safe guarding the environment and to maintain ecological as well as protect various social concerns.
- Out of the total harness able potential of about 24,000 MW, a potential to the tune of 20,912 MW already stands allotted under various sectors. The State has been accelerating the pace of Hydropower development through the active involvement of both the public and private sectors. A potential of about 10,596.27 MW has already been harnessed so far under various sectors.
- Though the private sector participation in terms of investments in this sector has been encouraging but the smaller projects has been reserved for investors from Himachal Pradesh only (up to 2 MW) and preference will be given for projects up to 5 MW.
Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Gram Jyoti Yojna (DDUGJY)
- The Ministry of Power, Government of India launched Deendayal Upadhyaya Gram Jyoti Yojna (DDUGJY) on 3rd December, 2014 for the electrification of rural households, separation of agriculture and non-agriculture feeders, strengthening and augmentation of Sub-Transmission and Distribution (ST & D) infrastructure in rural areas, including metering at distribution transformers, feeders and consumers end. The core objective is to ensure reliable and quality power supply in rural areas.
PRADHAN MANTRI SAHAJ BIJLI HAR GHAR YOJNA (SAUBHAGYA):
- Ministry of Power, Govt. of India launched Pradhan Mantri Sahaj Bijli Har Ghar Yojna (SAUBHAGYA) on 11th October, 2017 to ensure last mile connectivity and electricity connection to all remaining households in the country. In Himachal Pradesh, Saubhagya scheme was also implemented to ensure last mile connectivity and electricity connection to all the remaining un-electrified households.
Allotment of Hydro Projects:-
- Two Hydroelectric Projects to the tune of 1229 MW i.e. Dugar HEP (449 MW) located in Chamba District on river Chenab and Jangi-Thopan-Powari HEP (780 MW) located in District Kinnaur on river Satluj have been allotted to National Hydro Electric Power Corporation (NHPC) and Satluj Jal Vidyut Nigam (SJVNL) on 7-08-2018 and 24-11-2018 respectively.
The Government of Himachal Pradesh on dated 19/09/2019 has notified following amendments in the existing hydroelectric policy.
- Penalty has been decided by Government of Himachal from minimum ` 20,000/MW to ` 20.00 lakh in case of any equity change, change of the name of the company without prior approval of the government.
- In respect of Sunni, Dam Project, Luhri Stage-I HEP (210 MW- on Sutlej) and Dhaulasidh HEP (66 MW- on Beas river , Hamirpur), debt equity ratio has been allowed to 80:20.
- For Luhri Stage-I , Dhaulasidh and Dugar ( Chenab- Chamba) , provision of reimbursement of 50 per cent SGST has been allowed.
Commissioning of Hydro projects in the State:-
- Three projects have been commissioned in the state namely Jeori, Shimla(9.60 MW), Raura, Kinnaur (12 mw) and Rala, Kinn aur(13 MW).
- Two projects namely, (Salum, Chamba- 9 MW and Kuwarsi, Chanab II -15 MW) are expected to be commissioned by March, 2020.
Himachal Pradesh State Electricity Board Ltd.
Schemes of HPSEB Ltd:
| Schemes | Status |
| Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Gram Jyoti Yojna (DDUGJY) | The work of three districts is completed and remaining is likely to be completed by March 2020. |
| Integrated Power Development Scheme (IPDS) | Overall 73 per cent progress of IPDS system strengthening scheme has been achieved. |
| Computerized Electricity Billing | More than 22,00,000 consumers of HPSEBL are benefiting. |
PROJECTS UNDER HPSEBL
- UHL STAGE–III HYDRO ELECTRIC PROJECT (100 MW)
- SAI KOTHI STAGE-I HEP(15 MW)- Chamba ( on Bairah Nallah , a tributary of ravi)
- SAI KOTHI STAGE-II HEP (16.50 MW)- Chamba
- DEVI KOTHI STAGE-II HEP (16 MW)-Chamba- Balsi nalah (tributary of Ravi)
- HAIL HEP(18 MW) – Chamba
- KUTHAR HEP (5 MW) – Chamba ( Ravi river)
- RASION HEP (18 MW ) – Kullu ( Beas)
- NEW NOGLI HEP (11 MW) – Shimla
- TIKKAR HEP ( 5 MW) – Mandi ( Beas)
PROJECTS UNDER OPERATION/ EXECUTION STAGE THROUGH HPPCL ARE AS UNDER:
1. Integrated Kashang HEP (243 MW):-
Integrated Kashang HEP (243 MW) envisages development of Kashang and Kerang Streams, tributaries of the river Sutlej. This project is near Powari village in kinnaur district. comprising four distinct stages as under:-
-Stage-I (65 MW) -Stage-II and III (130 MW) -Stage-IV (48 MW)
- Detailed Project Report (DPR) of Kashang Stage – IV (48 MW) in district Kinnaur and Chirgaun Majhgaon HEP (60 MW) in district Shimla are under advance stages of appraisal with DoE Government of Himachal Pradesh.
2. Sainj HEP (100 MW):- on river Sainj, a tributary of River Beas in Kullu District of Himachal Pradesh. The project comprises of a diversion barrage on the river Sainj near village Niharni and underground power house on right bank of river Sainj near village Suind.
3. Sawra Kuddu HEP(111 MW):- on the Pabbar River in Shimla District (Himachal Pradesh) near Rohru. The Project is being financed by Asian Development Bank except Head Race Tunnel (HRT) Package, which is being financed by Power Finance Corporation (PFC) out of equity contribution by the State Government.
4. Shongtong Karcham HEP (450 MW) :- on the river Sutlej in District Kinnaur of Himachal Pradesh with diversion barrage, near village Powari, and underground power house, located on the left bank of the river Satluj near village
5. Chanju HEP-III (48MW) and Deothal Chanju HEP (30 MW) :-on Chanju stream which is a tributary Baira and Sieul of Ravi River in Chamba.
– Deothal Chanju HEP (30 MW) has also been developed on Deothal stream, a tributary of Baira of Ravi basin ( Chamba district).
6. Renuka ji Dam HEP (40 MW): Renukaji Dam project, conceived as a drinking water supply scheme for the National Capital Territory of Delhi, envisages construction of 148 metre high rock fill dam on river Giri at Dadahu in Sirmaur district and a power house at toe of Dam.
-The project has been declared as “National Project” by Govt. of India and is eligible to be funded by Govt. of India/ beneficiary states to the extent of 90:10 of the project cost. After persistent request by state govt. National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi has agreed to fund 90 % cost of power component of the project.
7. Surgani Sundla HEP (48 MW): The scheme has been envisaged to use the tail water (used water)of Baira Suil HEP for the Generation of 48 MW of Power. This project is in salooni Tehsil of Chamba District.
8. Dhamwari Sunda HEP (70 MW) : on Pabbar river in Distt. Shimla.
9. Thana Plaun HEP (191 MW): on river Beas in Mandi District of Himachal Pradesh.
10. Nakthan HEP (460 MW) : on Parbati River ( tributary of Beas) in Barshaini village Kullu.
11. Kishau Multipurpose Project (660 MW): Kishau Dam Project is proposed across River Tons (a tributary of River Yamuna) along the border of Uttarakhand and Himachal Pradesh. The Project has been declared as “National Project” by Govt. of India & is eligible to be funded by Govt. of India/beneficiary states to the extent of 90:10 of the project cost.
12. Triveni Mahadev HEP (78 MW) : on Beas river in Distt. Mandi.
Triveni Mahadev HEP (78 MW) in district Mandi, Gyspa Dam Project (300 MW) in district Lahul & Spiti and Bara Khamba HEP (45 MW) in district Kinnaur are in different stages of investigation.
Two projects totalling installed capacity of 350 MW shall be taken up in 3rd phase and preliminary survey and investigation works are being taken up for these projects. Pre feasibility reports (PFR) Lujai (45 MW) in district Chamba, has been prepared and work for pre-feasibility reports of Khab HEP (305 MW) in district Kinnaur shall be taken up shortly.
Solar Projects:
HPPCL has set up a 5 MW Berra Dol solar power plant, near Shri Naina Devi Ji Shrine in District Bilaspur. The work was awarded to M/s Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited and the contract agreement was signed on 22.07.2017. The plant has been successfully synchronized with HPSEBL grid on 07.12.2018. The project has operated since 04.01.2019. HPPCL has generated 8.58 million units of electricity from this project & revenue generated by sale of power till 31.12.2019 was `3.53 crore. HPPCL intends to set up another solar power plant of 10 MW capacity at Aghlor in District Una. The Detailed Project Report of the scheme is under preparation.
H.P. POWER TRANSMISSION CORPORATION LIMITED
Himachal Pradesh Power Transmission Corporation Limited (HPPTCL) is an undertaking of Govt. of Himachal Pradesh with a aim to strengthen the transmission network in Himachal Pradesh and to facilitate evacuation of power from upcoming generating plants.
Green Energy Corridor-I (GEC-I) funded by KfW amounting to 57 million Euro has been signed in October, 2015.
HIMURJA : HIMURJA: since 1989 HIMURJA has made concerted efforts to popularize renewable energy programmes throughout the State with financial support of Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE), Government of India and State Government. Efforts are continued for promotion and providing of renewable energy devices like Solar Solar Photovoltaic applications, Solar Cooker, solar water heating system etc. HIMURJA is also assisting the Government for exploitation of Small Hydro (upto 5 MW) in the State.
HIMURJA has made concerted efforts to popularize renewable energy programmes throughout the State with financial support of Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE), Government of India and State Government. HIMURJA is also assisting the Government for exploitation of Small Hydro (upto 5 MW) in the State.
HYDRO ELECTRIC PROJECTS BEING EXECUTED BY HIMURJA MHEPs
Following programmes are launched by Himurja:
Himurja is operating Micro Hydel projects at Lingti (400KW), Kothi (200 KW), Juthed (100 KW), Purthi (100 KW), Sural (100 KW), Gharola (100 KW), Sach (900 KW) and Billing (400 KW) which are under generation.
-As per decision of the Government, Micro Hydel projects namely, Lingti (400KW), Purthi (100 KW), Sural (100 KW), Gharola, Sach (900 KW) and Billing (400 KW) have been transferred and handed over to HPSEBL for operation. Other projects, namely Bara Bhangal (40 KW) and Sarahan (30 KW) have also been executed by HIMURJA.
Small Hydro Electric Projects Upto 5 Mw Capacity Being Executed Through Private Sector Participation
During the current financial year, 4 projects with an aggregate capacity of 13.80 MW have been commissioned up to December, 2019. Anticipated achievement up to March, 2020 will be about 20.00 MW. For the financial year 2020-21, capacity addition of 20.00 MW has been targeted.
Micro Hydel Projects up to 100 KW programme and Projects under State Sector
As on December 2019, 55 micro Hydel projects were allotted.
Important Policy Initiatives
- With view to harness hydro power potential in the State, some of the policy highlights as a part of ease of doing business are given below:
- Hydro Power Policy amended in 2018.
- It is mandatory for State Electricity Board to purchase power produced by hydro projects with capacity up to 10 MW.
- The generic tariff applicable in case of Hydro Power Projects (HEPs) up to 25 MW will be from the date of the commissioning and not from the date of implementation agreement.
- Wheeling charges/open access charges will not be levied for HEPs up to 25 MW capacity, enabling them to sell power on competitive rates outside the state also.
- Rationalization of royalty rates for allotment of new projects.
- Reduction in upfront premium and capacity addition charges.
- Nominal charges for Government/ Forest land announced.
Other important facts for prelims
- Sanjay Vidyut Pariyojna Hydroelectric Project in Kinnaur district ( Bhabha river ) is completely underground project.
- It is a 120 Megawatt project, containing 3 units each of 40 Megawatt. The power project is completed and became operational in the year, 1989- 1990.
- Rongtong HEP ( 2 MW) in Rangrik, Lahaul Spiti is one of the highest in the world. It is constructed on Rongtong river, tributary of Spiti river ( which is further tributary of Sutlej river).
- 1,500 MW Nathpa Jhakri hydro electric power project (NJHEP). It is built on river Sutlej in Kinnaur dist of HP. It is managed and run by SJVN ( Sutlej Jal Vidyut Nigam).
- Karcham Wangtoo HEP – 1000 MW , on Sutlej river
PARBATI HEP ( 1320 MW) : Parbati river ( Tributry of Beas ) - Former prime minister Atal Bihari Vajpayee had laid the project’s stone on December12, 1999.
- Earlier , It was planned to be a 2051 MW project divided into three stages i,e. Parbati stage I ( 731 MW), Parbati stage II ( 800 MW) and Parbati stage III ( 520 MW).
- Later on, Parbati stage I ( 731 MW) was scrapped due to technical issues.
- Thus after the scrapping of stage I, now the total capacity of Parbati HEP is reduced from 2051 earlier to 1,320 MW. This project is under NHPC.
Chulha power project or Uhl Stage III (100 MW)
|
CHAPTER 12. TOURISM AND TRANSPORT
- The contribution of the tourism sector to the State GDP is about 7 percent which is quite significant. The State is endowed with all the basic resources necessary for thriving tourism activity like geographical and cultural diversity, clean and peaceful environment and beautiful streams, sacred shrines, historic monuments and the friendly and hospitable people.
- As on 31st December, 2019 about 3,679 hotels having bed capacity of about 1,03,053 are registered with the department. In addition, there are about 2,189 Home Stay units registered in the State having about 12,181 beds.
- To give boost to the Tourism in the State, Asian Development Bank (ADB) has approved loan assistance worth US $ 95.16 million to HimachalPradesh for development of tourist infrastructure in the State.
- Department of Economic Affairs, Government of India has accorded approval for a new Tourism Project costing 1,892 crore.
Swadesh Darshan Scheme : The Government of India, Ministry of Tourism has sanctioned ` 8,685 lakh for the project, “Integrated Development of Himalayan Circuit in H.P.” under Swadesh Darshan Scheme. Total 12 tourism developments have been sanctioned under this scheme.
- Tourism Department has submitted a DPR of `45.06 crore for the development of Temple Complex, its Path and Pilgrimage Transport System of Maa Chintpurni Temple in Distt Una under PRASHAD Scheme to Ministry of Tourism, Govt. of India. PRASHAD stand for Pilgrimage Rejuvenation and Spiritual Augmentation Drive.
- The Department of Tourism is encouraging private sector to develop tourism related infrastructure in the State under Public Private Partnership (PPP). These includes ropeway project Adi Himani-Chamundaji, DharmshalaMecloedganj, Bhunter to Bijli Mahadev and Palchan to Rohtang RopewayProjects.In addition, to the department has also signed a MOU with Punjab Government for the ropeway from Sri Anandpur Sahib Ji to Shri Naina Devi Ji.
Publicity
Tourism Department prepares different types of promotional publicity material like brochures/pamphlets, posters, calendars, blow ups etc. and participates in various tourism fairs and festivals organized in the country and abroad. This department is also promoting tourism through promotional films and Social Media platform like Face book, Twitter and You Tube.
Civil Aviation
To attract high end tourist in the State, regular flights are taking place from the three existing airports i.e Jubbarhatti (Shimla), Bhunter (Kullu) and Gaggal (Kangra) in Himachal Pradesh. The Government is making sincere efforts for expansion of these airstrips.
Proposed International Airport, Nagchala, Balh valley
|
– To promote tourism in the state and to facilitate the visiting tourists as well as local people, State Government has also started helitexi service with effect from June,2018 from Shimla-Chandigarh-Shimla airport on Monday, and Friday of every week.
Nai Raahein Nai Manzilein
The State Government has launched a new scheme “Nai Raahein Nai Manzilein” with an outlay of ` 50.00 crore for the development of unexplored areas from tourism point of view. Bir-Billing district Kangra, Chansal Shimla, Janjehli Mandi, Larji Reservoir, Pong Dam have been identified for developing Eco Tourism, Adventure Tourism Water Sports and Ski Tourism in the State and two new tourism sites are also been developed at Kangnidhar (Mandi) & Rohtang Tunnel (Solang Nallah Side) under this scheme.
Sustainable Tourism
- UNESCO defines sustainable tourism as “tourism that respects both local people and the traveller, cultural heritage and the environment”.Tourism policy
- Earlier in 2013, the State had come up with the Sustainable Tourism Development policy.
- New policy : Government of Himachal Pradesh Tourism Sector Policy 2019
This policy has been framed to achieve sustainable development goals (SDGs), particularly SDGs 8 and 12 through various objectives directed towards the socio-economic growth of host communities, offering quality experience to travellers, protection of the natural-cultural environment and state’s destinations, and creating an investment friendly environment for private investors.
Himachal Pradesh Tourism Development Corporation (HPTDC)
- HPTDC is a pioneer in the development of tourism infrastructure in Himachal Pradesh. It provides complete package of tourism services, including accommodation, catering, transport, conferencing & sports activities having the largest chain of finest hotels restaurants in the State with 55 hotels having 991 rooms with 2,304 beds.
Transport and Communication
Roads and Bridges (State Sector):
- Starting almost from a scratch the State Government has constructed 38,984 kms. of motorable roads (inclusive of jeepable and track) till November, 2019.
National Highways (Central Sector)
- At present, 2,592 kms. of 19 National Highways are the main lifelines of the State Road network out of which 1,238 kms. length has been maintained/ developed by State Public Works Department.
- Beside above, the National Highway Authority of India has developed/ maintained 785 kms. of 5 National Highways and are under various stage for implementation.
- 569 Kms. length of 3 National Highways are developed/ maintained by Border Road Organization.
Railways
- There are only two narrow gauge railway lines connecting Shimla with Kalka (96 kms.) and Jogindernagar with Pathankot (113 kms.)
- One 33 kms. broad gauge railway line from Nangal Dam to Charuru in District Una upto December,2019.
PROPOSED BHANUPALI-BILASPUR-KULLU MANALI-LEH RAILWAY LINE
|
Him Darshan Express train


- The Ambala division of the Northern Indian Railway on 25 Dec 2019 started the Him Darshan Express train between Kalka and Shimla stations, as a Christmas gift to the people. It aims to promote tourism and provide a delightful experience to the passengers on the world heritage Kalka-Shimla section.
- The train has six modern and first-class AC vista-dome coaches with glass rooftop to have a panoramic view of the hilly region and one First Class coach. Each vistadome coach will have the capacity of 15 people, while the First Class coach has the seating capacity of 14 passengers.
- Booking for the vistadome coaches will be available through the passenger reservation system, but booking for the First Class coach of this special train will only be done through manual counters available at the Kalka and Shimla stations.
- Other trains normally run between Kalka and Shimla every day. ‘Toy train’ is the popular name for it.
ROAD TRANSPORT
- Himachal Road Transport Corporation (HRTC) has a fleet strength of 3,086 buses, 75 Electric Buses, 21 Taxies & 50 Electric Taxies plying bus services on 2,984 routes with coverage of 6.33 lakh kms daily (up to 31st October,2019).
For the benefit of people the following schemes remained in operation during the year:-
| Scheme | Benefit to card holder |
| Green Card Scheme | 25 percent discount in fare, if the journey under taken by passenger is of 50 km. The cost of this card is `50 and having its validity for two years. |
| Smart Card Scheme | The cost of this card is `50 having its validity for two years. This card having 10 percent discount in fare and also valid in HRTC Ordinary, Super Fast, Semi Deluxe and Deluxe buses. In Volvo and AC buses discount is to be allowed from 1st October to 31st March, in every year. |
| Samman Card Scheme | The discount of 30 percent in is allowed in ordinary buses to senior citizen of the age of the 60 years or more. |
| Free Facility to Women | Women have been allowed free travelling facility in HRTC ordinary buses on the occasion of “Raksha Bandhan” and “Bhaiya Dooj”. Muslim women have been allowed free travelling facility on occasion of “Id” and “Baker Id”. |
| Discount in fare to
Women |
The Corporation has also allowed 25 percent discount in fare in ordinary buses within the State to the women. |
| Free Facility to Students of Government Schools | Govt school students up to +2 classes have been allowed free travelling facility in HRTC ordinary buses. |
| person with serious disease | Free travelling facility to cancer, spinal injury, kidney and dialysis patients along with one attendant in HRTC buses for the purpose of medical treatment on referral slip issued by the Doctor within and outside the State. |
| Free Facility to the Special abled persons | If one is having disability of 70 percent or more along with one attendant within State.
|
| Gallantry Awardees | The Gallantry Award winners have been allowed free travelling facility in HRTC’s ordinary buses in addition to Delux Buses in the State. |
| Luxury Buses | HRTC is plying 51 owned and 39 buses super luxury (Volvo / Scania) and 24 luxury AC buses under Wet-Leasing scheme to interstate roads to provide better transport facility to the public. |
| 24X7 Helpline | 24×7 HRTC/ Private Bus Passenger’s helpline No.94180-00529 and 0177-2657326 have been introduced to lodge and address the complaints of passengers. |
| Taxies on sealed roads | Taxies Services have also been introduced by the HRTC in Shimla Town for public on sealed/ restricted roads |
| Tempo travellers | HRTC introduced 11 tempo traveller under wet- leasing scheme to major Tourist localities of the State in order to provide comfortable journey to the Tourist/ general Public. |
| Free travelling facility to the families of Martyrs | The HRTC is providing free travelling facility in ordinary buses to the Widows, children up to the age of 18 years, parents of armed force personnel and Para Military troops who were martyred on duty. |
| electric buses to tourist place | The HRTC has introduced electric buses for the tourist and visitors to the famous tourist places. |
| Facility of wheelchair | For the benefit of special abled person, wheel chair has been provided at 30 bus stands |
| Facility of Sanitary pad |
For the benefit of women Sanitary pad vending machines have been installed at 30 bus stands and in future will be provided in other bus stands . |
IF HORTICULTURE AND HYDRO-POWER MAKE UP THE BODY OF THE HIMACHAL PRADESH ECONOMY, TRANSPORT CONSTITUTES ITS―NERVES.
- As on December, 2019 the State has a total of 16,53,343 transport and non transport vehicles which have been registered.
Transport Policy 2014
The mission of the transport policy stated that it shall be the endeavor of the government to provide state of the art transportation facilities to the travelling public with high standards of comfort and safety. The main objective of the policy is to:
- To provide connectivity to the remotest corners of the State.
- Encourage most modern state of art goods transport vehicles entering the market for handling the farm and non-farm produce most efficiently and cost effectively for achieving export oriented growth;
- Mainstream Road safety concerns in the overall transport planning.
- Reduce environmental externalities of transport in Himachal Pradesh by developing suitable tax and non tax incentives and disincentives that encourage environment friendly transport and discourage polluting and unsafe vehicles;
- Alternate modes of transport like cable cars, trams and non-mechanised modes will be encouraged to achieve sustainable transport development overtime.
Significant achievements of the transport Department during the year 2019- 20 are as under:
Water Transport
- Water Transport Activities like passengers, cargo & tourists, water sports and Shikaras to be developed in Chamera, Koldam & Govind Sagar Lake for both Cargo & Passenger Transport.
Driving Training School (DTS) and Pollution Check Centre:-
- Transport department has given licenses to 262 driving training schools in the state which include 10 DTS of ITI, 12 HRTC and 240 private driving training schools. Beside 92 pollution check centres has also been authorized in the state.
Employment Generation
- Transport Department has fixed a target of employment generation for the year 2019-20 to 23,500 people out of which direct employment to 19,226 people have been provided up to December, 2019.
Implementation of FAME India Scheme:-
- 50 electric buses were sanctioned by Govt. of India under FAME-India Scheme for Shimla Town and now all these 50 Electric buses are plying in Shimla Town.
Note : Fame India stands for faster Adoption & Manufacturing of (Hybrid &) Electric Vehicles
Ropeway and Rapid Transport Corporation
- Newly setup Ropeway and Rapid Transport Development Corporation will be working on the following projects:-
- Passenger Ropeway Village Jana Kullu, District Kullu.
- Mass Rapid Transit System (M.R.T.S) to decongest cities in H.P. i:e Shimla, Manali and Dharamsala.
Electric Vehicle Policy:-
- It aims to provide incentives for electric vehicle consumers, manufactures as well as to the Charging Stations.
Road Safety Measures-
- The rate of road accidents has reduced as compared to the figures of last year as per table below.
ATAL TUNNEL (Rohtang Tunnel)
Why it is named after former PM Atal Bihari Vajpayee?
How long is the tunnel, and what is special about it ?
What is the status of the work (upto December 2019)?
So, is all-winter connectivity to Ladakh around the corner ?
*Telephone every 150 metres |
CHAPTER 13 : SOCIAL SECTOR
Education
- literacy rate of HP in 1971 : 31.96 per cent
- literacy rate of HP in 2011 census : 82.80 percent (89.53 per cent for males &75.93 percent for females).
| ASER stands for Annual Status of Education Report. This is an annual survey that aims to provide reliable estimates of children’s enrolment and basic learning levels for each district and state in India. ASER has been conducted every year since 2005 in all rural districts of India. It is the largest citizen-led survey in India. It is also the only annual source of information on children’s learning outcomes available in India today. |
ASER, 2019
- In all respects enrollment of children in government schools is higher relative to private schools. The enrollment of girl children for 15-16 age group is highest (82.9 per cent) for government school.
- If we only consider private school then enrollment in 7-10 age group is highest that is 48.1 per cent for boys and 41.8 per cent for girls as compared to other age groups.
- Percentage for children not in school is 2.4 percent boys in age group of 15-16 years.
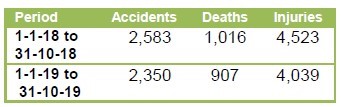
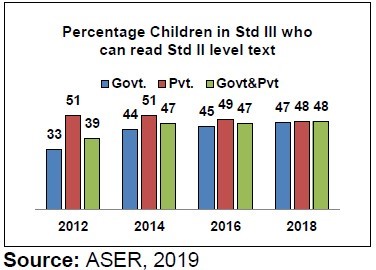
- Above table shows the variation in children’s reading levels within a given grade. For example, among children in Std III, 2 percent cannot read letters, 9.2percent can read letters but not words or higher, 15.7 percent can read words but not Std I level text or higher, 25.4percent can read Std I level text but not Std II level text, and 47.8 percent can read Std II level text.
Elementary Education
- The policies of the Government in the field of elementary education are implemented through the Deputy Directors of Elementary Education and Block Primary Education Officers at district and block level respectively.
- At present up to 31.12.2019 there are 10,721 Primary Schools and 2,049 government middle schools. Out of which 10,716 Primary Schools and 2,039 middle schools are functioning in the state.
| Ø In June 2020, HP govt has decided to regularise the services of teachers would benefit about 6,500 PTA (parent- teacher association), 3,300 PAT (primary assistant teacher ) and 97 para teachers serving in various government schools. |
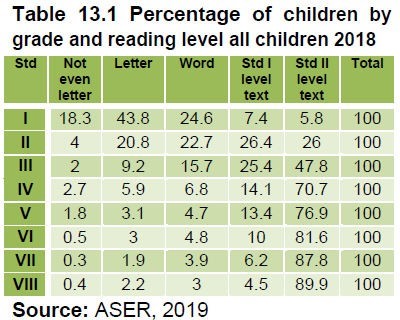
- The improvement in reading level can be observed from the above figure. In 2012 only 39 per cent of children of class III for both Pvt. and Govt. school were able to read class II standard level text, whereas it improved in 2018 where 48 per cent of class III standard children were able to read class II level text.
How HP Govt is increasing the student’s enrolment in school :
- To increase enrolment and to reduce the dropout rate and further to enhance the retention rate of the children in these schools, following scholarships and other incentives are being provided :
- State Sponsored Schemes for Elementary Education are given in the table below :
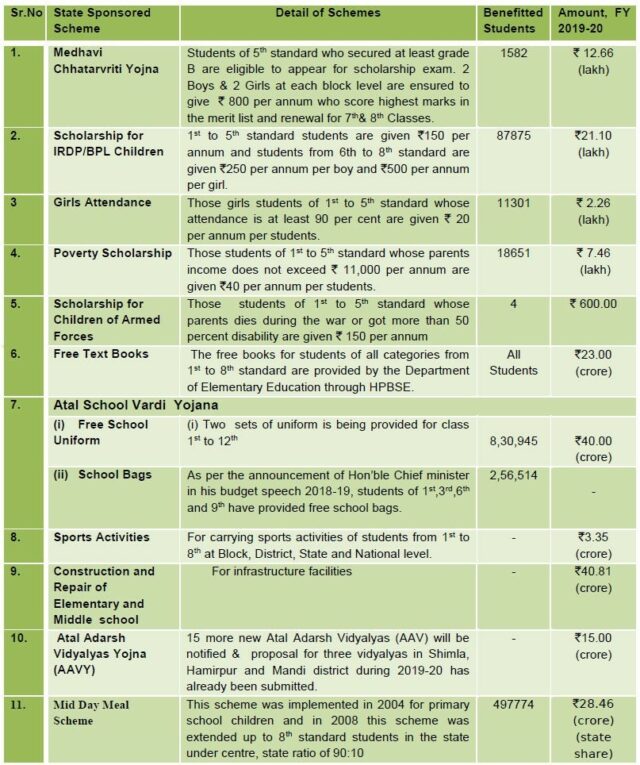
Learning Outcomes: The State government has provided subject and class wise learning outcomes developed by the NCERT to all elementary school teachers and they have been asked to teach in such a manner that the desired learning outcomes are attained by the students in each competency.
Teacher App: The State government has launched teacher app to make teaching learning more interesting and joyful.
- Padhe Bharat Badhe Bharat: launched in 2004 by HRD ministry, To teach with play way method flash cards, reading cards, charts, worksheets / workbooks, story books, cursivewriting worksheet learing resources at primary level have been provided to enhance their basic skills in Language and Arthmatic.
- Under National Initiative for School Heads’ and Teachers’ Holistic Advancement (NISHTHA), 354 Key Resource Persons (KPRs) and State Resource Persons (SRPs) have been trained by national resources group from NCERT. All the teachers at elementary level are being trained under NISHTA by the trained KRPs/RRPs. Government of Himachal Pradesh provided Mathematics and English kit to all Primary schools. Teachers have been trained for the use of these kits.
Rashtriya Avishkar Abhiyan (RAA)
- Science and Mathematics (Elementary and Secondary) developed by NCERT have been provided to selected schools.
- Activities under RAA in selected lab schools: i) Establishing mathematics laboratories. ii) Strengthening of existing science labs.
iii) Developing Science Parks with the help of experts in lab schools. Introducing BaLA (Building as learning aid) features related to mathematics and science learning on the wall and other available space. Developing Vermi compost plants. iv) Preparing students for Regional Mathematics Olympiads & Children Science Congress (CSC).
Kasturba Gandhi Balika Vidyalya (KGBVs)
- KGBV is a residential girls’ secondary school run by the Government of India for the weaker sections in India. It aims to provide educational facilities for girls belonging to Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, Other Backward Classes, minority communities and families below the poverty line in Educationally Backward Blocks.
- KGBVs have been opened in educational backward blocks of the State to enrol and provide free board and lodging facilities to out of school SC, ST and minority girls in school. There are ten Kasturba Gandhi Balika Vidyalayas (KGBVs) functioning in Himachal Pradesh. Eight KGBVs are in District Chamba, one each in district Shimla and Sirmour. Kasturba Gandhi Balika Vidyalaya are functioning under model- III, in which hostel facility is provided in the existing govt. schools. There is a provision of housing 50 girls in each KGBV hostel.
- The State Government has proposed up gradation of six KGBVs of district Chamba and one KGBV of Shimla from class VI to XII as per scheme of Government of India. Project Approval Board (PAB) has approved up gradation of seven KGBVs in the State. Currently 150 girls are residing in girls hostel and 850 girls from class 6th to 12th are in KGBVs. All these hostels are attached with Government Senior Secondary School.
Senior Secondary Education
Up to December, 2019, there are 931 Government High schools, 1,866 Government Senior Secondary Schools and 138 Government Degree colleges including 7 Sanskrit colleges, 1 SCERT, 1 B.Ed. college and 1 Fine Art College running in the State.
SCHOLARSHIP SCHEMES
Aim : To improve the educational status of the deprived sections of the society.
- Ambedkar Medhavi Chhatarvrity Yojna :
Under this scheme the scholarship is being given to the top 1,000 meritorious students of SC category and top 1,000 meritorious students of OBC on the basis of Matric examination conducted by HPBSE for 10 +1 and 10+2 classes in recognised institution within or outside of the State (Amount : `10,000 per student per annum). - Swami Vivekanand Utkristha Chhatarvrity Yojna:
Under this scheme 1,000 top meritorious students of General category declared as such in the result of Matric and 10+1 Examination conducted by HPBSE on merit basis for 10+1 and 10+2 classes are awarded the scholarship studying in school recognising within or outside the state is given `10,000 per student per annum. - Thakur Sen Negi Uttkristha Chhatarvrity Yojna:
Under this scheme, the scholarship is being given to the top 100 boys and 100 girl students of ST category on the basis of the Matric result conducted by HPBSE on merit basis for 10+1 and 10+2 classes in school recognising within or outside the State `11,000 per student per annum. - Maharishi Balmiki Chhatarvrity Yojna:
The bonafide Himachali girl students belonging to Balmiki families whose parents are engaged in unclean occupation are being given scholarship, under this scheme 9,000 per girl student per annum beyond Matric level to college level and for professional courses in Himachal Pradesh irrespective of their status (Government or Private). - Indira Gandhi Utkrishtha Chhatervriti Yojna:
Under this scheme, 150 meritorious students for post plus two courses for studying in colleges or doing professional courses shall be awarded ` 10,000 per year per student purely on basis of merit and without any income ceiling. - Sainik School Scholarship:
The scheme is applicable to the bonafide H.P. students in the Sainik School Sujanpur Tihra from class VI to XII. - NDA Scholarship Scheme:
The NDA scholarship at different rates is being given to the Cadets of Himachal Pradesh who are getting training at National Defence Academy, Khadakwasla. - Mukhya Mantri Protsahan Yojna:
This scheme has been started during the year 2012-13 and one time 75,000 will be given to all students of State who are selected and take admission for a degree course in any Indian Institute of Technology or All India Institute of Medical Sciences and post graduate diploma course in any Indian Institute of Management and Indian Insititute of Science (IISC) at Banglore. - Rashtriya Indian Military College Scholarship:
This award is given to the ten bonafide Himachal Pradesh students, two from each class VIII to XII in RIMC, Dehradun, `20,000 per year per student. - IRDP Scholarship Scheme
A sum of `300 per month for 9th and 10th class, `800 per month for +1 and +2 Class, `1,200 per month for College/Day scholar students and `2,400 per month for Hostellers is being given to those students who belong to IRDP families and studying in Government/ Government Aided Institutions. - Scholarship to the children of Armed Forces Personnel Killed/ disabled during wars.
A sum of `300 (boys) and `600 (girls) per month for 9th and 10th class, ` 800 per month for 10+1 and 10+2 Class, `1,200 per month for College/ University/ Day scholar students and `2,400 per month for hostellers is being given to Children of Armed Forces Personnel martyred/ killed/ disabled in different operations/ war. - Post Matric Scholarship to SC/ST/OBC students (Centrally Sponsored Scheme)
The students belongs to Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribles whose parents annual income is up to `2.50 lakh and Other Backward Classes students whose parents annual income is up to `1.00 lakh are eligible for full scholarship (i.e. Maintenance allowance + full fee) for all courses and they are studying in Government/ Government Aided Institutions. - Pre-Matric Scholarship to Other Backward Classes students.
This scholarship will be awarded to those students from class 1st to 10th whose parents/ guardians income from all sources does not exceed `2,50,000 per annum. A sum of `100 per student per month for day scholar students and `500 per month for hostellers is being given. - Pre-Matric Scholarship to SC students.
This scholarship will be awarded to those students whose parents/ guardians income from all sources does not exceed `2.50 lakh per annum. A scholarship of `3,000 per student per annum to Day scholars and `6,250 per annum to hostellers of class IX and X is being given. - Pre-Matric Scholarship to ST students.
This scholarship will be awarded to those students whose parents/ guardians income from all sources does not exceed `2.00 lakh per annum. A scholarship of `2,250 per student per annum to Day scholars and `4,500 per annum to hostellers of class IX and X is being given. - Incentive to SC/ST girl students for secondary education.
Under this Centrally Sponsored Scheme SC/ ST girl students who take admission in 9th Class after passing Middle Standard Examination from H.P. Board School Examination. The amount of incentive under this scheme is `3,000 and will be given in the shape of a Time Deposit. - Merit cum means Scholarship Scheme for Students belonging to Minority Community (CSS).
This Scholarship is for the Minority students belonging to Muslim, Sikh, Christian, Budhhist communities, whose parents/ guardians income from all sources does not exceed `2.50 lakh from all sources and student should not have less than 50 percent marks. - Post–Matric Scholarship Scheme to students belonging to Minority community(CSS):-
This Scholarship is being given from XI to Phd. level in Govt./recognized private school/college/ institute including technical/vocational courses for the Minority students belonging to (Muslim, Sikh-, Christian, Budhhist and Parsi ).The annual income of the parent or guardian of the beneficiary should not exceed ` 2.00 Lakh from all sources and student should have not less than 50% marks in the previous final examination. Student must pass the examination from Govt. / Govt.-aided institutions. - National Means-cum-Merit Scholarship (CSS):-
The Central sponsored Schemehas been started by Govt. of India, Ministry of Human Resource Development Department of School Education and Literacy Secondary Scholarship Division, New
Delhi. The Scheme is being implemented through Principal, SCERT, Solan. ( SCERT – State council for education research and training)
Expansion of Sanskrit Education
- Tremendous efforts are made to promote Sanskrit Education by the State Government as well as Centre Government. The details are as under:-
- Award of scholarships to students of High/ Senior Secondary Schools studying Sanskrit.
- Providing grant for the salary of Sanskrit Lecturers for teaching Sanskrit in Secondary Schools.
- Modernization of Sanskrit Schools.
- Grant to State Government for various schemes for promotion of Sanskrit and for research/ research projects.
Teachers Training Programmes
- The teachers training programmes are used to equip in-service teachers with the latest techniques/ teaching methods.
- Seminars/re-orientation courses are being conducted by State Council of Education Research and Training, Solan, Government College of Teacher Education Dharamsala, the Himachal Pradesh Institute of Public Administration, Shimla, National Institute of Educational Planning and Administration, Centre for Cultural Resources and Training, National Council of Educational Research and Training, New Delhi, Regional College of Education, Ajmer and Chandigarh.
- Approximately 2,700 teaching and non-teaching staffs have been trained during 2018-19.
Yashwant Gurukul Awas Yojna
In order to provide suitable residential accommodation to the teachers posted in High/Senior Secondary Schools of Tribal and hard areas of the state the scheme is being implemented in 61 identified schools of the State.
Free Text Books
The State Government is providing free text books to the students of 9th and 10th classes belonging to SC, ST, OBC and BPL categories. During the year 2019-20 `11.90 crore have been spent for this purpose and 1,03,134 students have been benefitted.
Free Education to Specially abled Children
Free education to the children having more than 40 percent specially abled is being provided in the State upto University level since 2001-02.
Free Education to Girls
Free education is being provided to girl students in the State up to University level including vocational and professional i.e. tuition fee is exempted.
Information Technology Education
Information Technology educations is being imparted in all Government Senior Secondary Schools on self finance basis through outsourcing where students have opted for IT education as an optional subject. The department is charging IT fee `110 per month per student. The students of SC (BPL) families are getting 50 percent fee concession of total fee. In the year 201920 about 72,647 students are enrolled in IT education subject out of which 6,773 SC (BPL) students are being benefitted under this scheme.
SAMAGRA SHIKSHA
From 2018-19 onwards, Integrated Rashtriya Madhyamik Shiksha Abhiyan (RMSA, ICT, Girls Hostels, Vocational Education, Scheme of Inclusive Education for Disabled at Secondary Stage (IEDSS)) has been merged in the Integrated Scheme for School Education (ISSE). The new merged scheme has been named as Samagra Shiksha.
The following schemes are running under Samagra Shiksha :
Rashtriya Madhyamik Shiksha Abhiyan
The Department has taken a lead in implementing the Rashtrya Madhayamik Shiksha Abhiyan (RMSA) at secondary level under Himachal Pradesh School Education Society (HPSES) on the sharing funding pattern 90:10. The activities under RMSA are being taken up to strengthen infrastructure in the existing secondary schools, training to in service teachers, self defence trainings and kala Utsav with Annual grant to schools in the State.
Information and Communication Technology (ICT) Project
In order to improve and strengthen the teaching learning activity by using smart class rooms and multi-media teaching aids, department has successfully implemented ICT in 2,137 Government High/ Senior Secondary Schools and five Smart Schools up to 2018-19. Government of India has introduced 200 more schools for the year 2019-20 and work is under progress.
Vocational Education
Under the National Skill Qualification Framework Scheme, starting of vocational education in 80 additional schools. MoU has been signed with 6 VTPs empanelled by National Skill Development Corporation and classes would be started in these schools from February,2020 (winter opening schools). Under this scheme: introduction of electronics and hardware, furnishing, apparel made ups & home, beauty and wellness, plumber etc. is to be introduced.
Inclusive Education for Specially abled at Secondary Stage
Inclusive Education for specially abled at Secondary Stage is commenced in the State in the year 2013-14. Under this scheme, 12 model schools have been established in all the districts and 18 special educators are engaged in these schools for imparting the Special Education to CWSN enrolled in the schools. Aids and Appliances, Free text books, escort allowance, braille and enlarge printing books have been supplied to the children with special needs during the year 2019-20.
Rashtriya Ucchtar Shiksha Abhiyan
The Rashtriya Ucchtar Shiksha Abhiyan has been implemented in the state to improve the higher education system. Under this scheme at present 36 Govt. Degree colleges will be accreditated from, NAAC Banglore during the year 2020-21.
Distribution of Net books/ Laptops:-
The department will distribute the laptops/Net books to 9,700 meritorious students of 10th and 12th class (4400-10th and 4400-12th class) of Himachal Pradesh Board of School Education, Dharamshala and 900 first division college students alongwith free monthly 1GB data Cards to strengthen teaching learning activities under student Digital Yojana/Sri Niwasa Ramanujan Digital Yojana for the academic session 2017-18.
Medha Protsahan Yojna
Selected meritorious economically weaker students of H.P & providing them coaching for CLAT/ NEET/IIT/JEE/AIIMS/AFMC/NDA/UPSC/SSC/Banking etc. In total 182 candidates (Graduate-34, Science-117, Arts-18 and 13 Commerce) against 500 are receiving coaching in 14 empanelled coaching institutions as per the choice of the students during the year 2019-20.
Installation of CCTV Surveillance System
In order to provide safety and security of the Govt. Educational institutions and Students, CCTV surveillance systems have been installed in 1,862 government schools during the year 2019-20.
Installation of Aadhar Enabled Bio Matric Attendance System (AEBAS)
The department has started the tendering process for the procurement of 2,552 Aadhar Enabled Bio Matric Attendance System (AEBAS) with the collaboration of HPSEDC. AEBAS will be installed in GSSS/GHS and Govt. Colleges.
Launching of on-line Him Shiksha Darpan Portal /App
Objectives : to automate the activities being carried out in the educational institutions/offices of Education Department with a view to improve the service delivery model, internal office efficiently as well as management facilitation.
Bachelor of Vocation
The B.Voc programme is running in 12 colleges of the State funded from State Share of ADB skill Project through HPKVN. The Department proposes to introduce B. Voc. Degree Programme in more colleges for the state with two new courses i.e. Banking, Financial Services and insurance & ITes.
Technical Education
- Department of Technical Education was established in the year 1968 and in July 1983, the vocational and Industrial and Training Institutes were also brought under the umbrella of this department.
- The department is providing education in the field of Technical Education, Vocational and Industrial Training.
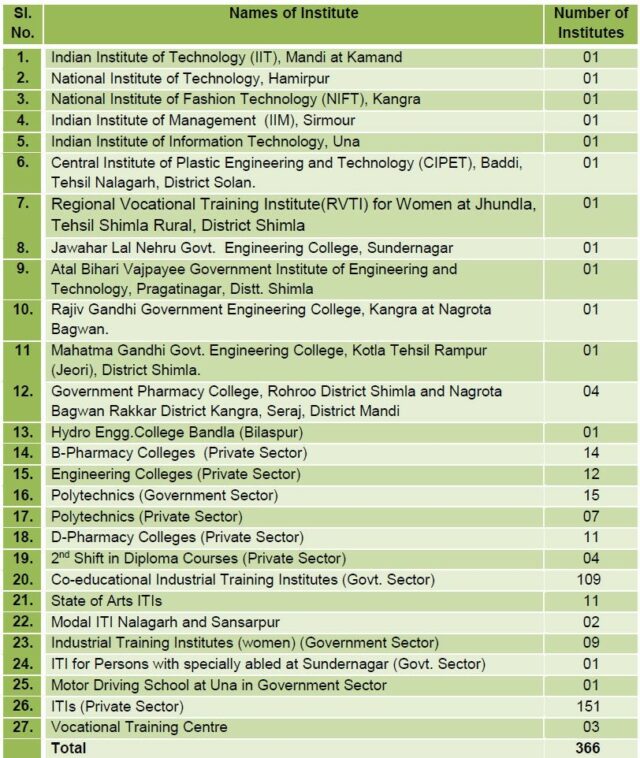
The present intake of students in the existing Institutions is as under: i) Degree Level 3,181 ii) B-Pharmacy 1,110 iii) Diploma Level 5,065 iv) Govt/Private ITI’s 48,509 Total 57,865
Technical Education quality Improvement programme phase-III (TEQIP-III)
- It was started from 01 April 2017 and will end in September 2020. Three colleges of the State viz JNGEC, RGGEC, ABVGIE and Him TU has been selected under project namely Technical Education Quality Improvement Programme Phase-III with project cost of `20.00 crore sanctioned to Him TU and `10.00 crore to each of the selected Institution.
- The Technical Education department has 132 Government I.T.Is, 1 driving Training & Heavy Earth Moving Machinery Operator School and 151 ITIs in Private sector.
During the year 2019-20 five new Government ITI’s made functional in year 2019-20 :
- ITI Kaulawala Bhood, Sirmaur.
- ITI Bhanjraruin District Chamba.
- ITI Utpur in district Hamirpur.
- ITI Rajoon in district Kangra.
- ITI Salooni in district Chamba.
Following new ITI’s will be made functional from the academic session 2020-21 :
Govt. ITI Amboya , District Sirmaur.
Govt. ITI Sataun, District Simaur
Govt. ITI Ladbharol, District Mandi
Dual System of Training DST
- DST includes theoretical training from ITIs and practical training from Industry partners thereBy strengthening industry and linkages and providing hand on experience to students on industry’s latest technologies and techniques.
- The DST to enhance the Skill Education among the trainees with the help of the industry has been made functional in ITI Solan in the year 2018-19.
- In the year 2019-20, the DST has been started in 08 Govt. ITI’s namely ITI Nadaun, Jogindernagar, Mandi, Garhjamula, Neharnpukhar, Shamshi, Solan and Govt. Model ITI Nalagarh.
Short Term Training Under HPSDP:
- Under Himachal Pradesh Skill Development Project(HPSDP), HPKVN has signed MoU with 38 Govt. Industrial Training Institute (ITIs) for providing NSQF (National Skills Qualifications Framework) aligned Short Term Skill Training to youth of Himachal Pradesh. At present, 4,500 candidates of 33 Govt. it is are undergoing training.
HEALTH
Health and Family Welfare
- Himachal Pradesh is comparatively in better position in health indicators than those of India.
- In Himachal Pradesh, Health and Family Welfare department is providing services which include curative, preventive, primitive and rehabilitative services through a network of Hospitals, Community Health Centers etc
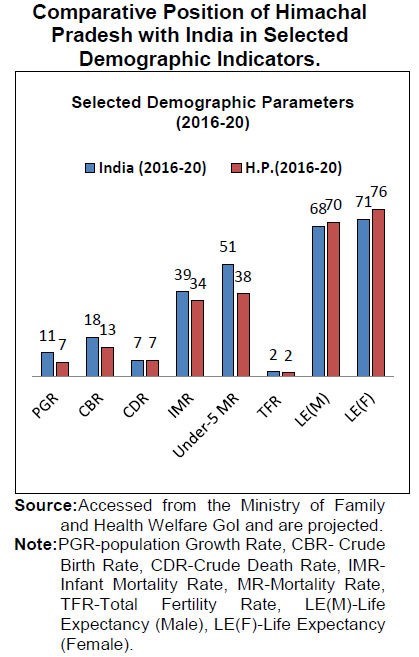
- Himachal Pradesh has projected on better position in all above mentioned indicators.
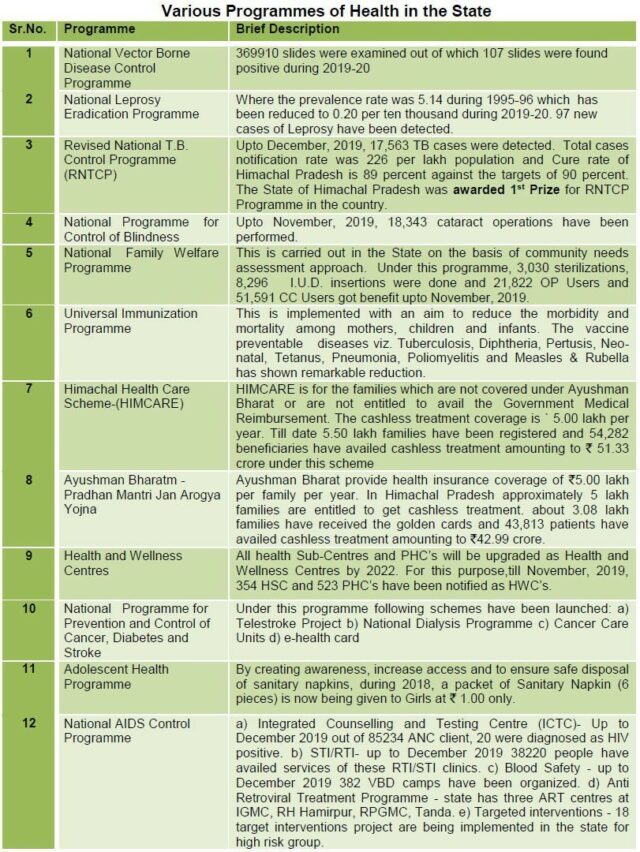
Medical Education and Research
The Directorate of Medical Education Training and Research was established in the year 1996-97.
Govt sector : At present the State has Six Government Medical Colleges & One Government Dental College in Shimla are functioning.
6 govt medical colleges are as follows :
- Indira Gandhi Medical College Shimla,
- Rajendra Prasad Medical College, Tanda,
- Yashwant Singh Parmar Government Medical College Nahan,
- Jawahar Lal Nehru Government Medical College, Chamba,
- Radha Krishan Government Medical College Hamirpur,
- Lal Bahadur Shastri Government Medical College Mandi Note: Except top two colleges, all other colleges are new.
Pvt Sector : One Medical College (Maharishi Markandeshwar University, Solan ) and four Dental colleges in private sector ( 1 each at Sundernagar and Paonta Sahib and 2 in Solan) are also functional in the State.
AYURVEDA
- Indian System of Medicines and Homoeopathy plays a vital role in the Health Care System of the State. The separate Department of Ayurveda was established in 1984 and Health Care services are being provided to the general public through 2 Regional Ayurvedic Hospitals, 31 Districts Ayurvedic Hospitals, 1 Nature Cure Hospital 1,178 Ayurvedic health centers, 3 Unani health centers, 14 Homoeopathic Health centers and 4 Amchi clinics.
- The department has inbuilt system of production of medicines through 3 Ayurvedic Pharmacies, at Jogindernagar (District Mandi), Majra (District Sirmaur) and Paprola (District Kangra).
- Rajeev Gandhi Government P.G. Ayurvedic College Paprola in Kangra district has an intake capacity of 60 students for B.A.M.S. degree and 39 seats of MD. The department has a B-Pharmacy (Ayurveda) college at Jogindernagar with intake capacity of 30 students.
Development of Herbal Resources
Four Herbal Gardens :
- Jogindernagar (District Mandi), Neri (District Hamirpur), Dumreda District Shimla) and Jangal Jhalera (Bilaspur) are functioning for propagating and conserving medicinal plants.
- Ministry of AYUSH, Government of India has established Regional-cumFacilitation Centre for North India at Research Institute in ISM, Joginder Nagar, District Mandi for the overall development of Medicinal Plants.
- A project for prevention of Anemia under Poshan Abhiyan is being run in three Development Blocks funded by Women and Child Development Department:
- Bangana, District Una.
- Bhoranj, District Hamirpur.
- Tissa, District Chamba.
SOCIAL WELFARE PROGRAMME
Social Welfare and Welfare of Other Backward Classes:
- The Social Justice and Empowerment Department of the State is engaged in socio-economic and educational uplift of scheduled castes, scheduled tribes, other backward classes, infirms, specially abled, orphans, children, widows, destitute, poor children and women etc.
- The following pension schemes are being implemented under social welfare programme:
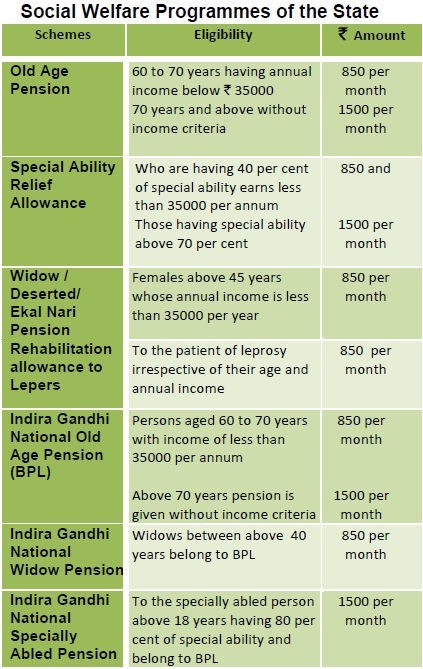
WELFARE OF SCHEDULED CASTES/ SCHEDULED TRIBES AND OTHER BACKWARD CLASSES : Under this programme, the important schemes implemented during 2018-19 are as under:-
- Award for Inter-caste Marriage: For elimination of the practice of untouchability with Scheduled Castes and non Scheduled Castes, the State Government encourages inter-caste marriages. Under this scheme, an amount of `50,000 per couple is given as incentive money.
- Housing Subsidy: Under this scheme the members of scheduled castes, scheduled tribes and other backward classes, minorities, person with special ability, widow/ destitute/ single women are given subsidy of `1,30,000 per family for house construction purposes and for house repair `25,000 to those whose annual income does not exceed from `35,000.
- Training and Proficiency in Computer Applications and Allied Activities: Under this scheme computer training are provided in the recognized computer courses to candidates belonging to BPL, SC, ST OBC, Minorities, Special Ability, single woman and widow or those whose annual income is less than `2.00 lakh. The department bears the training cost not exceeding `1,350 per month per candidate and `1,500 for special abled candidates balance cost if any is borne by the candidate.
- Follow up Programme: Under this scheme, `1,300 per beneficiary is being provided for purchase of tools for carpentry, weaving and leather works and `1,800 for purchase of, sewing machine to scheduled castes, scheduled tribes and other backward classes whose annual income does not exceed from `35,000 per annum.
- Compensation to Victims of Atrocities on Scheduled Castes/ Scheduled Tribes Families under SCs/STs (POA) Act-1989: Under the rules of the above Act monetary relief is granted to those scheduled castes, scheduled tribes families who become victims of atrocities committed by the member of other communities due to caste consideration, relief amounting to 85000 to `8.25 lakh is provided to the victims of atrocity, which depends upon the nature of atrocity.
IMP FACT : The district of Bilaspur, Kullu, Mandi, Solan, Shimla and Sirmaur are the predominantly Scheduled Castes population districts where Scheduled Castes concentration is above the State average. These six districts taken together account for 61.09 percent of the Scheduled Castes population in the state.
WELFARE OF SPECIALLY ABLED :
Department is implementing Comprehensive Integrated Scheme named “ASEEM” (A Scheme for Enabling, Empowering and Mainstreaming of the Specially Abled) for persons with special abilities.
- Specially Abled Scholarship This Scheme is applicable to all categories of special abled students including hearing impaired persons having special ability of 40 percent or above without considering their family income. The rate of scholarship varies from `625 to 3,750 per month.
- Marriage Grant to Individuals Marrying Persons with Special Abilities: To encourage able bodied young men or girls to marry the specially abled boy or girl having not less than 40 percent special ability, a marriage grant of `25,000 to those who are special abled with 40 to 69 percent and `50,000 to those who are special abled with more than 70 percent is provided by the State Government.
- Awareness Generation and Orientation: Provision has been made to organize block and district level composite camps for representative of NGOs working for persons with special abilities, SHGs and representative of PRIs at grass root level. In these camps medical certificates, aids and applications are provided to persons with special abilities. A part from this all the schemes being run for persons with special abilities are publicized in these camps.
- Self Employment: Special abled persons having special ability of 40 percent and above are provided loans by the Himachal Pradesh Minorities Finance and Development Corporation for setting up small ventures.
- Skill Enrichment: Vocational rehabilitation training to PWDs through selected ITIs is provided in identified trades. Training is free of cost and stipend `1,000 per month is paid by the department.
- Scheme of Awards: Provision of incentives to best performing special abled individuals and private employers providing employment to maximum special abled in their organization has been made. Best performing individuals are to be given cash award of `10,000 each. Best private employer is to be provided cash incentive of `5,000.
- Institutions of Children with Special Needs: Two institutions at Dhalli and Sundernagar have been set up in the State for providing education and vocational rehabilitation services to visually and hearing impaired children.
- Sepcial ability Rehabilitation Centres (DRCs): Two Special ability Rehabilitation Centres have been set up at Hamirpur and Dharamshala under NPRPD. These centres are being run through DRDA Hamirpur and Indian Red Cross Society, Dharamshala respectively.
(NPRPD : National Programme for Rehabilitation of Persons with Disabilities.
( DRDA District Rural Development Agency)
WOMEN, CHILD AND GIRLS WELFARE
Various schemes are being implemented for the welfare of women in the Pradesh.
a) Mahila Shakti Kendra
Mahila Shakti Kendra scheme is approved under Beti Bacho Beti Padhao at block level in the districts Una, Kangra, Hamirpur, Shimla, Solan, Sirmaur, Bilaspur, Mandi and Chamba. The objectives of the scheme are to empower rural women through community participation. Student volunteers will play an instrumental role in awareness generation regarding various important Government schemes/programmes as well as social issues.
b) Mukhya Mantri Kanyadaan Yojna: Under this programme marriage grant of `51,000 is being given to the guardians of the destitute girls for their marriages provided their annual income does not exceed `35,000.
c) Self Employment assistance for Women: Under this scheme `5,000 are provided to the women having annual income less than `35,000 for carrying income generating activities.
d) Widow Re-marriage Scheme: The main objective of the scheme is to help in rehabilitation of widow after re-marriage. Under this scheme an amount of `50,000 as grant, is provided to the couple.
e) Mother Teressa Asahay Matri Sambal Yojna: The aim of this scheme is to provide assistance of `6,000 per child per annum to the destitute (Poor) women belonging to the BPL families or having income less than ` 35,000 for the maintenance of their children till they attain the age of 18 years. The assistance will be provided only for two children.
f) Vishesh Mahila Utthan Yojna: This is 100 percent State Plan Scheme for training and rehabilitation of women physically & sexually abused in the State. There is a provision to provide stipend `3,000 per month per trainee.
g) Beti Bachao Beti Padhao scheme: This scheme had been launched in 100 districts of India including Una district of Himachal Pradesh. In the year 2016-17 the scheme has been started in Kangra and Hamirpur districts of Himachal Pradesh. During the financial year 2017-18 under Beti Bachao Beti Padhao Scheme five districts were selected i.e. Solan, Sirmour, Shimla, Bilaspur and Mandi of Himachal Pradesh with the objective of preventing gender biased sex selective elimination, ensuring survival, protection and education of the girl child. This scheme is an initiative to arrest and reverse the trend of an adverse and declining child sex ratio. Through this process, efforts are being made to create awareness among masses about the adverse effects of declining sex ratio.
h) Beti Hai Anmol Yojna
Under this scheme Post Birth Grant of `12,000 is provided to two girls only belonging to BPL families and scholarships are provided from 1st class to graduation level for their education. The rates of scholarships ranging from `450 to `5,000 per annum.
- i) Scheme for adolescent girls (SAG) :
Scheme for Adolescent Girls (SAG) has been universalized w.e.f.01.04.2018 and has totally replaced the Kishori Shakti Yojana. The scheme is being implemented through Anganwari Services of Umbrella ICDS platform and Anganwadi Centres are the focal points for the delivery of services. The scheme aims to support ‘out of school Adolescent Girls’ of 11-14 years age to successfully transition back to formal schooling or bridge learning, improving their nutritional and health status, promote awareness about health, hygiene, nutrition and upgrading various skills like home skills, life skills, vocational skills and guidance on existing public services. The cost sharing ratio of the scheme is 90:10 between the Centre and the State.
j) Pradhan Mantri Matru/Matri Vandana Yojna (PMMVY))
It is a Central sponsored scheme. The cost sharing ratio of the scheme is 90:10 between the Centre and the State. Under this scheme, a cash incentive of `5,000 would be provided directly in the account of Pregnant Women and Lactating Mothers in three installments for first living child subject to fulfilling specific conditions relating to maternal and child health. The mother should not be less than 19 years of age to avail this scheme.
k) One Stop Centre
One Stop Centre is a Central Sponsored Scheme. The main objective of the scheme are to provide integrated support and assistance to women affected by violence, both in private and public spaces under one roof; and to facilitate immediate, emergency and non-emergency access to a range of services including medical, legal, psychological and counselling support under one roof to fight against any forms of violence against women. In Himachal Pradesh One Stop Centres have been setup at Solan district.
In financial year 2018-19 Government of India has approved One Stop Centre for Mandi district.
l) Sashakat Mahila Yojna
In the budget speech of financial year 2017-18, new scheme Sashkat Mahila Yojana has been started. The scheme will focus on promotion of socio-economic empowerment of rural women by creating awareness about their right and facilitating institutional support for enabling them to realize their right and develop/utilize their full potential. The scheme will cover all 11-45 years of females.
m) Saksham Gudiya Board Himachal Pradesh
Government of Himachal Pradesh has constituted Kannya Sashkti Karan and Kalyan Board. Now the name of the Kalyan Board has been changed to Saksham Gudiya Board Himachal Pradesh. Its main objevtive is to look after the welfare of the girl child.
n) Bal/Balika suraksha yojna and foster care programme :
An amount of `2,000 per child per month is sanctioned in favor of foster parents for maintenance of children and `300 per child per month are sanctioned on account of additional assistance from the State.
o) Child Protection Scheme
The state have 45 Child Care Institutions, comprising of 38 Children Homes, 2 Observation Home-cum-Special, Home-cum-Place of safety, 4 Open shelters and 1 Shishu Grih.
p) Mukhymantri Bal Udhar Yojna
Financial assistance is provided to children after leaving Child Care Institutions for pursuing Higher/professional education.
q) Integrated Child Development Services
The department is providing Supplementary Nutrition, Nutrition and Health Education, Immunization, Health check-ups Referral Services and Non Formal Pre-School Education on the basis of 90:10 ratio by centre and state.
r) Supplementary Nutrition Programme
Supplementary nutrition is provided in Anganwari Centres to children, pregnant/ lactating mothers and BPL adolescent girls on 90:10 ratio by centre and state.
Trends in Social Sector Expenditure in Himachal Pradesh:
- The increase in expenditure on social services sector affirms the commitment of the government towards social well-being.
- The expenditure on social services (education, health and others) by State as a proportion of Gross Domestic Product (GDP) increased to 16 per cent from 7.68 per cent, during the period 2014-15 to 2019-20 (Advanced EstimateA).
- An increase has witnessed across all social sectors during this period. For education, it increased from 4.12 per cent in 2014-15 to 4.75 per cent in 2019-20 and for health from 1.25 to 1.66 per cent.
- The share of expenditure on social services out of total budgetary expenditure increased to 34.14 per cent in 2019-20 (A) from 25.73 per cent in 2014-15.

