Himachal Pradesh Economic Survey 2019-20 Chapter 7
( HP ECONOMIC SURVEY 2019-20)
CHAPTER 7: AGRICULTURE AND HORTICULTURE
Agriculture
- Agriculture is the main occupation of the people of Himachal Pradesh and has an important place in the economy of the State.
- Himachal Pradesh is the only State in the country whose 89.96 percent population (Census 2011) lives in rural areas.
- Agriculture/ Horticulture provide direct employment to about 69 percent of total workers of the State.
- Agriculture is an important source of State Income (GSDP). About 73 percent of the total GSDP comes from agriculture and its allied sectors.
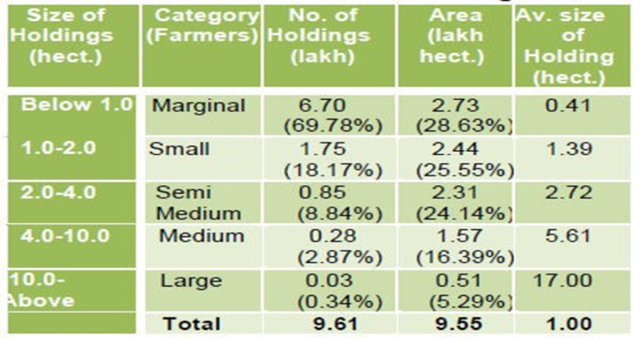
- Out of the total geographical area of State (55.67 lakh hectare), the area of operational holdings is about 9.55 lakh hectares and is operated by 61 lakh farmers.
- The average holding size is about 1.00 hectare.
- About 80% of total cultivated area is rainfed.
- Distribution of land holdings according to 2010-11 Agricultural Census :
- 95 % = Small and Marginal farmers.
- 71 % = semi medium and medium farmers and only 0.34 % = large farmers.
CATEGORY OF FARMERS :
Distribution of Land Holdings
- Rice, Wheat and Maize are important cereal crops of the State.
| Kharif | Rabi | |
| Important ( major) cereal crops | Rice and Maize | Wheat |
| Minor crops | Ragi, millet | |
| important pulses | Urd, Bean, Moong, Rajmash | Gram Lentil ( Chana Dal) |
| important oilseed crops | Groundnut, Soyabean and Sunflower | Rapeseed / Mustard and Toria |
Agro-climatically the State can be divided into four zones viz.:-
Sub Tropical, sub-mountain and low hills.
- Sub Temperate, Sub humid mid hills.
- Wet Temperate high hills.
- Dry Temperate high hills and cold deserts.
The Agro-climatic conditions in the State are favorable for the production of cash crops like seed potato, off-season vegetables and ginger.
- Almost half of the rainfall is received during the Monsoon season
- The State received an average rainfall of 1,251 mms ( 125.1 cm).
- Kangra district gets the highest rainfall followed by Chamba, Sirmaur and Mandi.
| The State Government is laying emphasis on production of off-season vegetables, potato, ginger, pulses and oilseeds besides increasing production of cereal crops, through timely and adequate supply of inputs, demonstration and effective dissemination of improved farm technology, replacement of old variety seed, promoting integrated pest management, bringing more area under efficient use of water resources and implementation of Wasteland Development Projects. |
Monsoon Season 2019 (June – Sep 2019
- For Himachal as a whole, the total rainfall during the entire monsoon season was 10 percent below the annual normal rainfall. Rainfall received was :
- Excess in Bilaspur,
- Normal in Hamirpur, Kangra, Kullu, Mandi, Shimla, Sirmour, Solan and Una,
- Deficient in Chamba ,Kinnaur and Lahaul Spiti.
|
Normal = -19% to +19% |
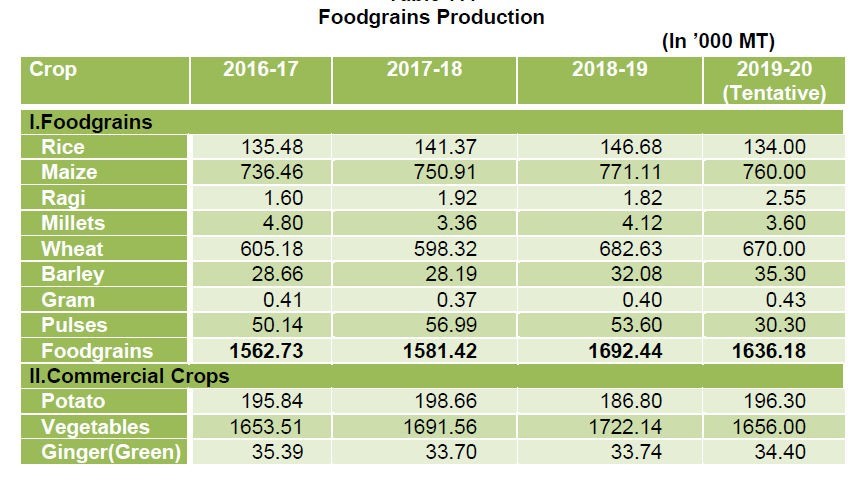
Crop Performance 2018-19 oThe year 2018-19 remained an average year.
- The foodgrains production was 16.92 lakh MT ( 15.81 lakh MT in 2017-18 ) o The production of Potato was 1.87 lakh MT ( 1.99 lakh MT in 2017-18). oThe production of vegetables was 17.22 lakh MT ( 16.92 lakh MT in 201718).
Crop Prospects 2019-20
- The food grain production target for 2019-20 is 36 lakh MT.
- An area of 26 thousand hectare was sown under different Kharif crops.
- The production of 17 lakh M.T. has been expected against the production target of 7.77 lakh M.T. for the Kharif 2018 season.
Growth in Foodgrains Production
- There is limited scope of increasing production through expansion of cultivable land. Like rest of the country, Himachal too has almost reached a plateau in so far as cultivable land is concerned. Hence, emphasis has to be on increasing productivity levels besides diversification towards high value crops. Due to an increasing shift towards commercial crops, the area under food-grains production is gradually declining as the area in 1997-98 which was 853.88 thousand hectares declined to 732.62 thousand hectares in 2018-19. Decreased area under food-grains production thus reflects loss in productivity.
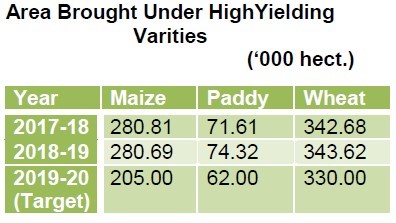
High Yielding Varieties programme (H.Y.V.P )
- In order to increase production of foodgrains, emphasis has been laid on distribution of seeds of high yielding varieties to the farmers. There are 20 Seed Multiplication Farms from where foundation seed is distributed to registered farmers.
- In addition, there are 3 Vegetable Development Stations, 12 Potato Development Stations and 1 Ginger Development Station in the State.
Plant Protection Programme:
- During each season, campaigns are organised to fight the menace of crop disease, insects and pest etc.
- The scheduled castes/ scheduled tribes, IRDP families’ farmers of backward areas and small and marginal farmers are provided plant protection chemicals and equipments at 50 percent cost.
- It is the approach of Agriculture Department to reduce consumption of plant protection chemicals by gradually switching to biological control of pests/diseases.
Soil Testing Programme:
- To maintain the fertility of the soil during each crop season, soil samples are collected from the farmers’ fields and analyzed in the soil testing laboratories.
- Soil testing laboratories have been established in all the districts (except Lahaul and Spiti), and four mobile soil testing vans/labs out of which one exclusively for the tribal areas is in operation for testing the soil samples at site.
- At present 11 soil testing labs have been strengthened, 9 mobile labs and 47 mini labs have also been setup by the department. The Government of India has launched a new scheme based on which the sample of soil shall be drawn on GPS basis. During the year 201920, 18,725 soil samples shall be analyzed.
- Soil testing service has also been included under P. Govt. Public Service Act, 2011 in which the soil health cards are being made available to the Farmers through online service.
Prakritik Kheti Khushal Kisan scheme/Yojna (PKKKS) under Zero Budget Natural farming:
- Under this scheme, the HP Government intends to encourage “Zero Budget Natural Farming”, so as to bring down the cost of cultivation. The use of chemical fertilizers and chemical pesticides will be discouraged. The budget provided for pesticides/ insecticides to the department of Agriculture and Horticulture will be used for providing bio-pesticides and bio- insecticides. A budget provision of ₹19.25 crore has been kept for 2019-20.
- The scheme is applicable only to the residents of the Himachal Pradesh only. The scheme is meant for the farmers.
PKKKS Benefits:
- 75% subsidy on drums which are required to make inputs for natural farming.
- Financial assistance of 50,000 to open natural resources store in village.
- Training and workshop to create awareness about natural farming for farmers.
Fertilizer Consumption and Subsidy:
- The level of fertilizer consumption in 1985-86 was 23,664 tonnes, which has increased to 57,555 MT in 2018-19. In order to promote balanced use of chemical fertilizers, a subsidy of `1,000 per MT on complex fertilizers have been allowed, use of water soluble fertilizers is promoted in a big way for which subsidy has been allowed to an extent of 25 percent of cost. About 51,500 MT of fertilizers in terms of nutrients are proposed to be distributed during 2019-20.
Agriculture Credit:
- HP govt is aiming to Provide better access to institutional credit for small and marginal farmers and other weaker sections to enable them to adopt modern technology and improved agricultural The banking sector prepares crop specific credit plans and the credit flow is monitored urgently in the meetings of the State level Bankers Committee.
INSURANCE SCHEMES
Crop Insurance Scheme :
- The State Government has introduced this scheme from Rabi, 19992000 season.
Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojna –
- launched since Kharif season 2016. The different stages of risk leading to crop loss due to preventing sowing, post harvest losses, localized calamities and losses to standing crops (from sowing to harvest) have been covered under this new scheme.
- The scheme is compulsory to loanee farmers and optional for the Non loanee farmers.
- Under Pradhan Mantrai Fasal Bima yogna, total No. of 2,70,772 farmers have been covered in Kharif 2018 and Rabi, 2018-19 seasons under PMFBY.
- A budget provision of ₹7.00 crores has been made for the year 201920 which is utilized for the payment of state share of premium subsidy.
Restructured Weather Based Crop Insurance Scheme. (R-WBCIS):
- launched since Kharif, 2016 season. The scheme intends to provide insurance protection to the cultivators against Natural Calamities which are deemed to adversely affect the Kharif crops during its cultivation period.
Seed Certification Programme:
- Agro-climatic conditions in the state are quite conducive for seed production. In order to maintain the quality of the seeds and also ensure higher prices of seeds to the growers, seed certification programme has been given due emphasis. Himachal Pradesh state Seed Certification Agency registers growers in different parts of the State for seed production and certification of their produce.
Agriculture Marketing:
- For the regulation of agricultural produce in the State, Himachal Pradesh Agricultural/ Horticulture Produce Marketing Act, 2005 has been enforced. Under the Act, Himachal Pradesh Marketing Board has been established. Himachal Pradesh has been divided into ten notified market areas.
- Its main objective is to safeguard the interest of the farming community. The regulated markets established in different parts of the State are providing useful services to the farmers.
- A modernised market complex at Solan is functional for marketing of agricultural produce, besides construction of market yards in different area.
- At present 10 market committees are functioning and 58 markets have been made functional. Market information is being disseminated through different media i.e. AIR, Doordarshan, print media and through net to farmers.
Tea Development:
- Total area under tea is 2,311 hectares with a production level of 8.77 lakh Kg achieved in 2018-19. Small and marginal farmers are provided agriculture inputs on 50 percent subsidy.
|
QUICK REVISION OF HISTORY OF TEA CULTIVATION IN HP
|
SOIL AND WATER CONSERVATION
MUKHYA MANTRI NUTAN POLYHOUSE YOJNA:
- In order to achieve faster and more inclusive growth in agriculture sector, government of Himachal Pradesh has started “Mukhya Mantri Nutan Polyhouse Yojna amounting to ₹. 59 lakh has been approved by the Govt. and submitted to NABARD for funding under RIDF-XXV.
- This scheme was started by CM Jairam Thakur in Budget 2019-20 ( last year) and under this scheme about 5000 poly houses will be constructed by providing 85 percent subsidy or a period of 4 years i,e 2019-20 to 2022-23.
DR.Y.S.PARMAR KISAN SWAROZGAR YOJNA :
- The scheme envisages setting up 4700 polyhouses and 2150 Drip/sprinklers irrigation units in the state. For this, 85 percent project assistance ( subsidy) is being provided to the farmers to set up polyhouses and drip/sprinklers irrigation units.
- Also for creation of water sources individually and collectively by a group of farmers, (low/ medium lift, pumping machinery) 50 percent subsidy shall be provided.
RASHTRIYA KRISHI VIKAS YOJNA (RKVY)
- RAFTAAR was initiated in 2007 as an umbrella scheme for ensuring holistic development of agriculture and allied sector. Till 2013-14, the scheme was implemented as an Additional Central Assistance (ACA) to State Plan Scheme with 100% central assistance. It was converted into a Centrally Sponsored Scheme in 2014-15 also with 100% central assistance. Since 2015-16, the funding pattern of the scheme has been altered in the ratio of 60:40 between Centre and States (90:10 for North Eastern States and Himalayan States).
- Now RKVY has been revamped as RKVY-RAFTAAR Remunerative Approaches for Agriculture and Allied sector Rejuvenation for the remaining period of the Fourteenth Finance Commission.
The main objectives of the scheme are as under:
- To strengthen the farmer’s efforts through creation of required pre and post-harvest agri-infrastructure that increases access to quality inputs, storage, market facilities etc.and enables farmers to make informed choices. 2. To provides flexibility and autonomy to states in the process of planning and executing Agriculture and allied sector schemes.
- To promote value chain addition linked production models that will help farmers increase their income as well as encourage production/productivity.
- To mitigate risk of farmers with focus on additional income generation activities-like integrated farming, mushroom cultivation, bee keeping, aromatic plant cultivation, floriculture etc.
- To attend national priorities through several sub schemes
- To empower youth through skill development, innovation and agrientrepreneurship based agri business models that attract them to agriculture.
The Government of India has allocated ₹ 24.10 crore in favour of Himachal Pradesh under Normal RKVY for the year 2019-20 as central share10% of (90%) and with matching State share ₹.2.68 crore, the total allocation for the year 2019-20 is ₹ 26.78 crore.
National Mission on Agricultural Extension and Technology (NMAET)
- National Mission on Agricultural Extension and Technology (NMAET) has been launched to make the extension system farmer-driven and farmer arrangement of technology dissemination. NMAET has been divided into four sub-missions.
- Sub Mission on Agriculture Extension (SAME).
- Sub Mission on Seed and Planting Material (SMSP).
- Sub Mission on Agriculture Machanization (SMAM).
- Sub Mission on Plant Protection and Plant Quarantine (SMPP).
- Note : It is a centrally sponsored scheme and the component will be in the ratio of 90:10 centre and state share respectively. Under the scheme a budget provision of ₹ 33.00 crore has been made for the year 2019-20.
NATIONAL MISSION ON SUSTAINABLE AGRICULTURE (NMSA):
- NMSA has been formulated for enhancing agricultural productivity especially in rain fed areas.
- Main deliverables under this mission are:
- Developing rain fed agriculture.
- Natural resources management.
- Enhancing water use efficiency.
- Improving soil health.
- Promoting conservation agriculture.
- Under the scheme a budget provision of ₹24.48 crore has been made for the year 2019-20.
NATIONAL FOOD SECURITY MISSION (NFSM):
- It is aimed to enhance the production of Rice, Wheat and Pulses.
- NFSM has been launched in the State from Rabi 2012 with two major components viz.NFSM-Rice and NFSM-Wheat.
- NFSM-Rice is in operation in three districts of state and whereas NFSM-Wheat in nine district with 100 percent assistance from Central Government.
- The aim of Mission is to increase production of Rice and Wheat through area expansion and productivity enhancement restoring soil fertility and productivity, creativity employment opportunities and enhancing level of farm economy in targeted districts.
- Under this scheme provision of `16.50 crore has been made for the year 2019-20.
PRADHAN MANTRI KRISHI SINCHAI YOJANA
- It aims to improve the Agricultural productivity.
- Micro-irrigation projects (“Har Khet Ko Pani”) and end-to-end irrigation solutions will be the key focus of this scheme.
- “The major objective of the PMKSY is to achieve convergence of investments in irrigation at the field level, expand cultivable area under assured irrigation, improve on-farm water use efficiency to reduce wastage of water, enhance adoption of precision-irrigation and other water-saving technologies”.
- Under this scheme a budget provision of `22.00 crore has been proposed for the year 2019-20 under state plan.
EFFICIENT IRRIGATION THROUGH MICRO-IRRIGATION SCHEME
- Aim : efficient system of irrigation
- The scheme was launched with an outlay of `154.00 crore over a period of 4 years starting from 2015-16 to 2018-19.
- Through this project 8,500 hectare area will be brought under Drip/ Sprinkler Irrigation System benefitting 14,000 farmers. The subsidy @ 80 percent for the installation of Sprinkler and drip irrigation system would be provided to the farmers.
- A budget provision of `25.00 crore has been made for this component for the year 2019-20.
UTTAM CHARA UTPADAN YOJNA
- Aim : to increase fodder production in the state,
- State Govt has launched this scheme for fodder development by bringing an area of 25,000 hectare under fodder production. Quality seed of fodder grasses, cuttings, and seedings of improved fodder varieties will be supplied on subsidized rates to the farmers.
- Subsidy on Chaff Cutters is available to the SC/ ST and BPL farmers.
- A provision of `5.60 crore has been made for year 2019-20 under this scheme.
MUKHYA MANTRI KHET SANRAKSHAN YOJNA
- Monkey and wild life menace causes huge loss to crops annually. Therefore, Government of Himachal Pradesh has introduced a scheme “Mukhya Mantri khet Sanrakhshan Yojna”.
- Under this scheme, a subsidy of 80 percent will be provided for solar fencing. Electric Current in the fence around the farms will be sufficient to keep away the stray animals, wild animals and monkeys from the farms.
- Under this scheme ₹ 35.00 crore has been provided for the year 2019-20. About 2000 hectares cultivated land will be fenced/ protected from wild/ stray animals and monkeys menace under this scheme.
MUKHYA MANTRI KISAAN EVAM KHETIHAR MAZDOOR JEEVAN SURAKSHA YOJNA
- This scheme was launched in 2015-16 to provide Insurance cover to the Farmers and Agricultural Laborers in the event of sustaining injury or death due to operation of farm machinery.
- In case of the death and permanent special ability, compensation of `1.50 lakh and in case of partial special abilities `50,000 will be provided to the affected farmers.
LIFT IRRIGATION AND BOREWELL SCHEME
- In most parts of the State, water has to be lifted for irrigation purpose.
- As an incentive to the farmers, Government has decided to grant 50 per cent subsidy for construction of Lift Irrigation Schemes and installation of Bore-Wells by individual or group of farmers for irrigation purposes.
- Under this scheme, financial assistance is available for construction of Low & medium lift irrigation systems, shallow wells, shallow bore wells, water storage tanks of different capacities, pumping machinery and water conveyance pipes to individual farmers or a group of farmers.
- A budget provision of `9.91 crore has been kept for the year 2019-20.
SAUR SINCHAYEE YOJNA
- Under this scheme, 90 percent assistance will be provided to small / marginal farmers for the installation of solar pumping machinery on individual
- 80 percent assistance will be provided to medium / big farmers for the installation of solar pumping machinery on individual
- 100 percent assistance will be provided if minimum Five farmers opted for installation of solar pumping machinery on community basis.
- Under this scheme, 5,850 agriculture solar pumping sets will be made available to the farmers.
- The total outlay for this scheme is ₹200 crore for next Five years. A budget provision to the tune of ₹30.00 crore has been kept for the year 2019-20.
JAL SE KRISHI KO BAL YOJNA :
- Under this scheme, check dams and ponds will be constructed. Farmers can use this water for irrigation purpose after construction of small lifting schemes or Flow Irrigation schemes on individual basis. Under this scheme, 100 percent expenditure would be borne by the Government for implementation of community based small water saving scheme. The total outlay for this scheme is ₹ 250.00 crore for next five years. A budget provision of ₹25.00 crore was kept for this for 2019-20.
HORTICULTURE
- The rich diversity of agro-climatic conditions, topographical variations and altitudinal differences coupled with fertile, deep and well drained soils favour the cultivation of temperate to sub-tropical fruits in Himachal.
- The region is also suitable for cultivation of ancillary horticultural produce like flowers, mushroom, honey and hops.
- This particular suitability of Himachal has resulted in shifting of land use pattern from agriculture to fruit crops in the past few decades. The area under fruits, which was 792 hectares in 1950-51 with total production of 1,200 tonnes increased to 2, 32,139 hectares during 2018-19. The total fruit production in 2018-19 was 95 lakh tonnes, while during 2019-20 (upto December, 2019) it has been reported as 7.07 lakh tonnes.
- During 2019-20, against the target of 1,950 hectares of additional area under fruits, 2113 hectares of area has actually been brought under the plantations. A total of 5.28 lakh different fruit plants distributed upto 31st December, 2019 during the year 2019-20.
- Apple is so far the most important fruit crop of Himachal Pradesh, which constitutes about 49 percent of the total area (1,12,634 hectares in 2017-18) under fruit crops and about 79 percent of the total fruit production.
- In warmer area of the State mango has emerged as an important fruit crop. Litchi is also gaining importance in certain regions. Mango and litchi are fetching better market prices.
Horticulture Development scheme :
- It is a major programme aiming at the creation and maintenance of infrastructural facilities in the rural areas for ensuring equitable access to the resources and inputs required for the promotion of all fruit crops.
Sub-Mission of Agriculture Mechanisation (SMSM) :
- Under this scheme, assistance is provided to the farmers for the purchase of various modern farm tools and machinery in form of back ended subsidy. State Agriculture Department, Himachal Pradesh is nodal Department of the scheme. During the year 201920 funds amounting to ₹14.83 crore has been allocated to the Department of Horticulture.
Marketing Intervention Scheme :
- The fruit producers should get better price of their produce therefore marketing Intervention Scheme is being implemented in the state. Under this scheme during the year 2019-20 the procurement price of apple is ₹ 8.00 per Kg. The procurement price of mango fruit is ₹ 6.50 per kg. of seedling mango upto 500MT, ₹7.50 per Kg. of Grafted mango upto 250 MT and ₹ 6.50 per Kg. of Unripe Achari Mango upto 50MT.
- In warmer areas Mango and litchi are fetching better market prices.
- In the midhill zone, the agro-climatic conditions are highly suitable for the successful cultivation of new fruits like kiwi, olive, pomegranate, pecan and strawberry.
Flower cultivation :
- To bring diversification in horticulture industry a total area of 47 hectares has been brought under flower cultivation upto 31.12.2019.
- 9 Farmers Cooperative Societies are functioning for the production and marketing of flowers in district Shimla (3), Kangra (2), Lahaul & Spiti (2), Solan (1) and Chamba (1).
- To promote flower cultivation two Tissue Culture Laboratories have been established under Model Flower Cultivation Centres at Mahogbagh (Chail, District Solan) and Palampur ,District Kangra. ‘Himachal Pushp Kranti Yojna and ‘Mukhya Mantri Madhu Vikas Yojna’ are two schemes in flower sector of Horticulture.
Ancillary horticultural activities
- Ancillary horticultural activities like mushroom and Bee keeping are also being promoted. During 2019-20 upto December, 2019, 245.79 MT of pasteurized compost for mushroom was prepared and distributed from the department units located at Chambaghat, Bajoura and Palampur. A total of 5,707 MT. of mushroom was produced in the state during the year upto December, 2019.
- Under the Bee keeping programme, 78 MT of Honey has been produced during the year upto 31.12.2019 in the state.
- To promote protected cultivation in horticulture, the state government has enhanced subsidy under Poly Houses from 50% to 85% and 72,099 Sq. meter area is targeted to be brought under Green Houses during year 2019-20.
- To protect fruit crops especially apple from hailstorms, the state government has enhanced subsidy on Anti hail nets from 50% to 80%. It is targeted to bring 3,01,047 Sq. meter area under Anti Hail Nets during the year 2019-20.
- The weather based Crop Insurance Scheme was initially launched in Himachal Pradesh during rabi season 2009-10. From the year 2017-18 name of the scheme has changed to Restructed Weather Based Crop Insurance Scheme (R-WBCIS).
- For the implementation of centrally sponsored scheme, Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (RKVY) during the year 2019-20, funds amounting to ₹399.94 lakh have been received from Govt. of India and has been allocated to the field functionaries and the work is under progress. Funds has been provided under ‘Infrastructure & Asset’ scheme amounting to ₹101.24 lakh for ‘Horticulture Development through Farm Mechanization’, ₹42.00 lakh for ‘Establishment of Mushroom units’ ₹73.70 lakh for ‘Creation of water sources’, ₹60.00 lakh for Pack Houses, ₹80.00 lakh for ‘Strengthening of Diganostic facilities and infrastructure for establishment of cleanplant stock and production of virus tested plant material of apple for distribution to farmers and ₹43.00 lakh for Establishment of High-tech nursery to boost production of fruit crop in sub-tropical areas of Himachal Pradesh under ‘Flexi Funds’ scheme.
- A newly launched scheme Himachal Khumb Vikas Yojna was launched during 2019-20 to promote mushroom cultivation in the State and ₹5.00 crore were received and further allocated to field functionaries.
- For the implementation of Mukhya Mantri Green House Renovation Scheme for replacement of poly film of old poly houses a sum of ₹ 1.00 crore were provided in the year 2019-20 and ₹20.00 crore have been allocated under “Installation of Anti-Hail Nets” scheme to protect the fruit crops from hail storms.
- ₹10.00 crore have been allocated under ‘Himachal Pushp Kranti Yojna’ during the year 2019-20.
Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH) :
- a Centrally sponsored scheme being implemented in the State by Department of Horticulture under which assistance is provided as back ended subsidy (for bankloans) @ 50 percent to farmers for carrying out various horticultural activities like cultivation of fruits, flowers, vegetables, spices and establishment of new gardens, Mushroom Production, Green House cultivation of High value flowers and vegetables, Anti Hail Nets, Horticulture Mechanization, Post Harvest Management etc.
Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojna-Per Drop More crop (PMKSYPDMC)
- A centrally sponsored scheme which is being implemented by state department of Horticulture, Himachal Pradesh since 2015-16.
- In the year 2017-18, the PMKSY-Per Drop More Crop guidelines were modified with a provision of subsidy @ 55 percent for small & marginal farmers and 45 percent for big farmers.
- The state is providing 25 percent additional state share to give
80 percent subsidy to small & marginal farmers. For the year
2019-20, GOI., has sanctioned ₹14.40 crore for PMKSY-PDMC. Till date (2015-16 to December,2019) 2588.07 hac. area has been covered under micro-irrigation benefitting 4,654 farmers.
Himachal Pradesh Marketing Corporation (HPMC)
- P.M.C. a State public undertaking was established in the Pradesh with the objective of marketing fresh fruits and vegetables, processing the unmarketable surplus and marketing the processed products. Since its inception, HPMC has been playing pivotal role in the life of fruit growers of the state by providing them remunerative returns of their produce.
- The Corporation has successfully commissioned 5 CA Stores in the following apple growing areas of District Shimla and Kullu namely Jarol Tikker, (Kotgarh) 640 MT, Gumma (Kotkhai) 640 MT, Oddi (Kumarsain) 700 MT and Patlikuhal (Kullu) 700 MT capable to store total 3,380 MT,s.
- Setting up of one modern vegetable pack house and cold room at Nadaun district Hamirpur and setting up of Pack house and cold room for packing grading of fruits, vegetables, flowers and culinary herb at Ghumarwin in district Bilaspur with 100 percent grant in aid of `7.89 crore are likely to be completed by March, 2020 for grading and storing of vegitables in the district of Hamirpur and Bilaspur.
- Grant in aid to the tune of `8.00 crore for the up gradation of Apple Juice Concentrate (AJC) Plant at Parwanoo has been received from Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority (APEDA) and work of up gradation has been successfully completed in year 2018 by undertaking trial production in the same year.In 2019 the commercial production of AJC was 1,012 M.T. undertaken from up graded plant, which is all time high production during one calendar year since the inception of the corporation in the year 1974.
- At Fruit Processing Plan (FPP), Jarol (Sundernagar) all time high production during one calendar was recorded in 2019 by producing 235.25 MT,s of AJC, since the inception of the corporation in the year 1974.
- HPMC has planned to enhance its existing capacity of Grading Storage and Processing of difference fruit produced in the state from the World Bank funded HP HDP Project, under this project the process of enhancing the existing storage capacity of CA Stores Jarol Tikker, Gumma and Rohru from existing 1,980 MT,s to 6,000 MT,s is under process.
| H.P. Horticulture Produce Marketing & Processing Corporation (HP State Government Undertaking) popularly known as HPMC was incorporated on 10th June, 1974 with the financial assistance of World Bank. The mandate of this organization was to provide postharvest facilities to the fruit growers of the state and to help them to get best returns for their produce from the market. |
ANIMAL HUSBANDRY AND DAIRYING
- Rearing of livestock is an integral component of rural economy.
- Under Mukhyamantri Arogya Pashudhan Yojna 1,251 veterinary dispensaries have been opened up to December, 2019.
- For improving the quality of sheep and wool, Government Sheep Breeding Farms at Jeori (Shimla), Tal (Hamirpur), and Karachham (Kinnaur) are supplying improved sheep to the breeders of the State. One Ram centre at Nagwain in district Mandi is also functioning where improved Rams are reared and supplied to breeders for cross breeding. The flock strength of these farms are 1,111 during the year 2019-20 upto December,2019 and 219 Rams were distributed to the breeders. In view of the increasing demand for pure Hoggets and the established popularity of the Soviet Marino and American Rambouillet in the pradesh, the state has switched over to pure breeding at the existing government farms in the state and 9 Sheep and wool Extension Centres continue functioning. During the year 2019-20, the wool production is likely to be 1,516 tonne.
- Angora rabbit farms are functioning at Kandwari (Kangra) and Nagwain (Mandi) for distribution of rabbits to the breeders. Here Pure breed German Angora rabbits are being bred on scientific lines
- Dairy production is an integral part of Animal Husbandry and forms part of the earning of small and marginal farmers in Himachal Pradesh. Upgradation of indigenous cattle is being carried out by cross breeding with Jersey and Holsten. In buffalo upgradation with Murral bull is being popularized. Artificial insemination with the latest technology of Deep Frozen Semen (DFS) is being practiced. Cross breed cows are preferred because of factors such as longer lactation period, shorter dry period and higher yields. During 2019-20 the “Uttam Pashu Puraskar Yojna” was implemented with the provision of `21.00 lakh.
Objective of the Uttam Pashu Puraskar Yojna Scheme:
|
- During 2019-20 under the Backyard Poultry Scheme,10 lakh dual purpose coloured strains chicks are likely to be distributed and 2,000 persons are targeted to impart training in poultry farming.
- One horse breeding farm at Lari in Lahaul and Spiti district has been established with the objective to preserve Spiti breed of horses. During the year 2019-20 up to December, 2019 59 horses have kept in this farm.
- One Yak breeding farm has been also established in the premises of horse breeding Lari. During the year 2019-20 up to December, 2019 the strength of yaks was 62 in this farm.
Dairy Entrepreneurship Development Scheme (Doodh Ganga Yojna):
- Doodh Ganga Scheme has been launched in collaboration with NABARD in the state since 25th september, 2009. The components of the scheme include:
- Establishment of small dairy units (units size comprise of 2-10 milch animals) bank loan of `00 lakh for purchase of 10 animals.
- Bank Loan to the tune of `00 lakh for purchase of milking machine/ bulk milk cooling units,
- Purchase of dairy processing equipments for manufacture of indigenous milk products, bank loan to the tune of `13.20 lakh.
- Establishment of dairy products transportation facilities and cold chain bank loan of `26.50 lakh.
- Cold storage facilities of milk products bank loan of `33.00 lakh.
- Dairy, marketing outlet/ Dairy parlour bank loan of `1.00 lakh
Pattern of Assistance
- Bank ended capital subsidy @ 25 percent of the project cost for general category and 33 percent for farmers of SC/ ST category.
- Apart from above, state government is providing additional subsidy of 10% for the purchase of crossbreed/Jersey cows and 20% for the purchase of indigenous cows to the benefiters of DEDS scheme.
National Project on Bovine Breeding
- Total `23.87 crore national project on Bovine breeding has been sanctioned by Government of India on 100 percent Central Assistance
Backyard Poultry Farming
To develop poultry sector in Himachal Pradesh, department is running following poultry development schemes especially in rural areas of the State.
Under Backyard Poultry Project, 3 week old Low Input Technology (LIT) birds are distributed among the poultry breeders on cost price
200-Chick Scheme:-Under this scheme the 540 poultry breeders belonging to BPL Families of Schedule cast Category are to be provided with inputs (like 200 days old LIT birds, feed for intial feeding, feeders & drinkers) worth Rs 10,000/ per beneficiaries. There is also provision of training regarding poultry management for the beneficiaries.
Rashtriya Gokul Mission (RGM)
- It is Rs`1.95 crore project launched by government of India for conservation and propagation of Sahiwal and Red Sindhi breeds through Embryo Transfer Technology (E.T.T) at Palampur.
Objectives
- Development and conservation of indigenous breed.
- Enhancement of milk production and productivity.
- Up-gradation cattle using elite indigenous breeds like, Sahiwal and Red Sindhi.
- Establishing of a Gokul Gram (integrated cattle development centers) in the state.
- Establishing of Murrah Buffalo
National Livestock Mission (NLM)
- It is a centrally sponsored scheme launched w.e.f. year 2014-15. The mission is designed to cover all the activities required to ensure quantitative and qualitative improvement in livestock production systems and capacity building of all stakeholders. Activities related to development of Small Ruminants i.e. sheep and goat, fodder development, risk management and poultry development are included in the scheme. State share is different for different components under this scheme.
Assistance to State for Control of Animal Diseases (ASCAD) :
- Under (ASCAD), the Central government has provided assistance to state government for control of contagious diseases to livestock on the pattern of 90 percent Central share and 10 percent State Diseases for which free vaccination is being provided to livestock owners are foot and mouth Disease, Haemorrhagic Septicemia Black Quarte, Enterotoxaemia, Peste Das Petitis Ruminants, Raniket Disease, Marek’s disease and Rabies under this project.
Shepherd Scheme:
- The local sheep is being crossed with good quality Rams of Rambouillet and Russian merino so that the quality as well as quantity of wool production can be increased. Hence, it is being proposed that these Rams should be provided to the sheep breeders at 60 percent subsidy.
BPL Krishak Bakri Palan Yona:
- Under this scheme it is proposed to distribute units of 11 Goats (10 female+1 male), 5 Goats (4 female + 1 male) and 3 Goats (2 female + 1 male) of Beetls Sirohi/ Jamnapari/ white Himalayan breeds respectively on 60 percent subsidy to landless, BPL category farmers to increase their income.
Integrated Sample Survey for Estimation of Production of Major Livestock Product:
- This survey is carried out in the state as per the guideline of Indian
Agricultural Statistical Research Institute (AHS Division) New Delhi. It provides a reliable database relating to livestock population. Integrated Sample Survey is being conducted since 1977-78 regularly every year with the aim :-
- To estimate season wise & annual milk, egg & wool production.
- To work out average population & yield estimates.
- To estimate dung production.
- To work out average feed & fodder consumption. To study trend of population, yield & production.
Livestock Census:
- Livestock census is being conducted quinquennially (every five years) by the government of India and so far, 20 such census have been conducted.
Milk Based Industries:
- P. Milkfed is implementing dairy development activities in the state. The H.P. Milkfed has 1,024 milk producers Co-operative Societies. The total membership of these societies is 43,250 out of which 205 woman dairy co-operatives are also functioning. The surplus milk from the milk producers is collected by village dairy cooperative societies, processed and marketed by H.P. Milkfed.
- At present the Milkfed is running 22 milk chilling centres having a total capacity of 91,500 litres milk per day and 11 milk processing plants having a total capacity of 1,00,000 litres milk per day.
- One milk powder plant of 5 metric tonne per day at Duttnagar in Shimla district and one cattle feed plant of 16 metric tonne per day capacity at Bhor in District Hamirpur has been established and functioning. The average milk procurement is about 77,000 litres per day from the villages through village dairy cooperatives. H.P. Milkfed is marketing approximately 27,397 litres of milk per day which includes milk supply to various prestigious dairies in bulk and supply to army units in Dagshai, Shimla, Palampur and Dharamshala (Yol) areas.
- P. Milkfed provides technical know-how, awareness activities in field of dairy by organizing seminars, camps in rural areas.
- The dairy development activities in Himachal Pradesh are based on two tier structure of dairy cooperatives. The basic unit of Anand Pattern is a village dairy cooperative where the surplus milk of the milk producer is collected and tested and payment made on the basis of the quality. HP Milkfed comes in second tier.
- Himachal Pradesh Government has increased milk procurement rates by `2.00 per litre w.e.f. 01.04.2019 thus giving direct financial benefits to 43,250 families associated with the Milk Federation.
H.P. Milkfed has initiated the following developmental activities :
- Processing plants of capacity 5,000 litres per day are being set up at Reckong Peo (Kinnaur), Nalagarh (Solan), Mohal (Kullu) and Jangal Beri (Hamirpur), Chamba, Rohru, Nahan, Una.
- Processing plants of capacity 20,000 litres per day are being set up in Mandi and Kangra
- P. Milkfed is marketing Him milk products such as milk powder, gee, butter, dahi, paneer and sweetened flavored milk, khoa under the name brand ‘Him’
- P.Milkfed has installed 40 AMCU (Automatic Milk Collection Unit ) in Shimla, Mandi and Kullu district under the centrally sponsored scheme NPDD(National Programme for Dairy Development) in 2018-19
New Innovations of Milkfed
- Himachal Pradesh Milkfed is manufacturing panjiri at ‘Panjiri Manufacturing Plant’ Chakkar (Mandi) to cater the need of the Welfare Department under ICDS
- 29,359 quintal of ‘Nutrimix has been supplied during 2018-19.
- Himachal Pradesh Milkfed has also supplied 4,905 quintals of Skimmed Milk Powder (SMP) and 18,189 quintals of bakery biscuit to Women and Child Welfare Department.
- P. Milkfed has also diversified its activities by manufacturing 400 quintals of sweets during Deepawali festival.
Upcoming milk processing plant by H.P. Milkfed
- Duttnager (Shimla): capacity – 50,000 Ltr/day (LPD ) which will be further enhanced to 70,000 LPD.
- Chakkar (Mandi) : capacity – 50,000 LPD
- Milkfed has introduced fortified Milk – Him Gauri with Vitamin A & D on 28.11.2019 in order to address the deficiency of Vitamin A & D in the state in collaboration with NDDB & TATA Trusts.
Wool Procurement and Marketing Federation:
- The main objective of the Federation is to promote the growth and development of wool industry in the state of Himachal Pradesh and to protect wool growers from exploitation by the middleman/traders. In pursuance to the above objective, the federation is actively involved in procurement of sheep and angora wool, sheep shearing at pasture level and marketing of wool. Sheep shearing is done with the imported automatic machines. During the year 2019-20 up to December, 2019 the sheep wool procurement was 82,697 kg. and the value of the same was `52.76 lakh.
FISHERIES AND AQUA CULTURE
- HP is the land of perennial rivers with oxygen rich water to support growth of fish.
- State’s linearly flowing rivers Beas, Satluj and Ravi receive many streams during their downward journey and harbour the precious cold water fish fauna such as Schizothorax, Golden Mahseer and exotic Trouts.
- The reservoir of Himachal Pradesh has the distinction of highest per hectare fish production in Govind Sagar and highest sale price value of fish catch in Pong Dam in the country.
- Cold water resources of the state have shown their potential with the successful completion of ambitious Indo-Norwegian Rainbow Trout farming project (Patlikuhl, kullu).
- The Department of Fisheries has constructed Carp as well as Trout seed production farms in the state to cater the requirement of reservoirs rural ponds and commercial farms in public as well as private sector.
- The Department of Fisheries has initiated many welfare schemes for the upliftment of fishermen. Fishermen are covered under insurance scheme where `00/1.00 lakh is given (in case of death/ permanent disability) in case of partial disability) and`10,000 towards hospital expenses and even losses to their gearand crafts are also being borne by the state government to the extent of 50 percent under “Risk Fund Scheme”. A contributory saving scheme has been initiated by the state government under this scheme Fisherman, state and centre is contribute equally .This fund is provided to the fisherman during close season.
- Under Blue Revolution, the Department of Fisheries has envisaged construction of 1,000 hectare new ponds and 1,000 trout units in the state by 2022. Central Sector Scheme of Blue Revolution is being shared in 90:10 between central and state government.Under Blue Revolution scheme during 2019-20 :
- Construction of 20 ha. new ponds/tanks will be done in private sector with financial assistance of `79.90 lakh.
- Establishment of 6 Trout Feed Mill in private Sector with financial assistance of `24.00 lakh in Kullu, Mandi, Chamba, Shimla and Sirmaur District for the production of high quality of fish in the State.
- Establishment of 6 Trout hatcheries in private Sector with financial assistance of `60.00 lakh.
- Establishment of 120 Trout farming units in the State.
- Matsya Mudra Scheme for aquaculture development in private sector
- Establishment of trout cages in Koldam reservoir in Govt,.sector
- Establishment of 3 retail outles for fish farming in the State
- Establishment of Recirulatory Aquaculture system in Government sector.
FOREST
- Forests in Himachal Pradesh cover an area of 37,947 Sq. Km. and account for 16 percent of total geographical area of the state. However, presently 28.60 percent of the total geographical areas support Forest cover.
(all lands, more than one hectare in area with a tree canopy density of more than 10% is called forest cover ).
| NATIONAL SCENARIO
India has a target of having 33 percent of its total area under forest and tree cover. The latest ‘India State of Forest Report (ISFR 2019) released by the |
| country’s environment minister Prakash Javadekar on December 30, 2019, revealed that the total forest and tree cover of the country is 807,276 square kilometres (which is 24.56 percent of the geographical area of the country) compared to 802,088 sq km (24.39 percent) in ISFR 2017. The report marked an increase of 5,188 sq. km. of forest and tree cover combined, at the national level, as compared to the previous assessment. |
- The main objective of Himachal Pradesh Forest Policy is the proper utilization of forests, conservation and extension. The aim of the Forest department is to enhance the forest cover in the state to 30 percent of its geographical area by 2030 to meet the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The plan programme taken up by the Forest department aims at fulfilling these policy commitments. Some of the important plan programme activities are as under:-
Forest Plantation:
- Forest plantation is being carried out under various state plan schemes such as Improvement of tree cover, and soil conservation, Compensatory Afforestation Fund Management and Planning Authority (CAMPA) as well as centrally sponsored scheme “National Afforestation Programme”, pasture and grazing lands of the state are being managed under state scheme development of Pasture and grazing lands. Van mahotsava at state, circle and division levels is also celebrated for educating the masses and creating awareness amongst all stakeholders regarding forestry and environmental concerns under New Forestry Scheme (Sanjhi Van Yojana). Apart from this, the department is organizing plantation drive involving local communities like Mahila Mandals, Yuvak Mandals, Local people and public representatives since 2018-19. During the current monsoon season, the department organized 5 days plantation campaign throughout the state w.e.f. 20th to 24th July, 2019 and target to plant 25 lakh was fixed. This drive gained a huge success and 1,18,932 people enthusiastically participated in the campaign and 26,47,146 plants were planted at 727 selected places. For the year 2019-20, plantation target of 9,000 hectares Including CAMPA and centrally sponsored schemes has been fixed out of which 8,475.23 hectares target stands achieved and remaining target would be achieved upto 31.03.2020.
Forest Management (Forest Fire Prevention & Management Scheme):
- Forest protection is being strengthened by equipping check posts at sensitive places with CCTVs to ensure electronic surveillance to curb forest offences. Fire fighting equipment and improved techniques are also being introduced and made available to all the forest divisions where fire is a major destructive element. Communication network for effective management and protection of forest wealth is very important. Keeping these factors in view, centrally sponsored scheme- Forest Fire Prevention & Mananagement Scheme (earlier known as Intensification of Forest Management Scheme) is being implemented in the state. During the year 2019-20 an outlay of `222.07 lakh has been approved as Central share (90%) and state share `24.67 lakh under Forest Fire Prevention and Management Scheme.
- Another scheme under state plan namely “Forest Fire Management Scheme” has been introduced with a budget provision of `100 lakh during 2019-20.
Experimental Silvicultural Felling:
- Forest wealth of Himachal Pradesh is estimated at more than `1.50 lakh crore. By the permission of Hon’ble Supreme Court of India the state has been allowed for silvicultural green felling of three species viz. Khair, Chil and Sal on experimental basis in three rangesNurpur range of Nurpur Forest Division, Bharari range of Bilaspur Forest Division and Poanta range of Poanta Forest Division under the supervision of Hon’ble Supreme Court Monitoring Committee constituted for the purpose.
- Note : A ban on green felling was imposed in 1996.
Schemes of forest / plantations :
-Van Mahotsava : 1-7 july every year, started by KM Munshi, union minister for agriculture in 1950.
-Sanjhi Van Yojana: 1998, 2001
–Smriti Van Yojana : it envisages tree plantation by people in specially designated areas on the occasion of their birthday, marriage anniversary or on death anniversary of their parents/ relatives/ elders.
Nagar Van Udyan Yojana – “Ek Kadam Hariyali Ki Or”-A Programme for Climate Smart Green Cities
- The vision of this scheme is to create at least one City Forest in each city having Municipal Corporation for providing wholesome, healthy living environment and contributing to growth of Smart, Clean, Green, Sustainable and Healthy Cities. Under this scheme 80 percent funds are to be provided by the National CAMPA Advisory Council (NCAC) and 20 percent by the State Government.
NEW SCHEMES :
i) Samudayik Van Samvardhan Yojna
-
- The main objective of this scheme is to ensure participation of local communities in conservation & Development of Forests through Plantation, Improving quality of forest and increasing the forest cover. The scheme will be implemented through existing JFMCs ( joint forest management committees).
- During 2018-19, 20 sites have been selected and 11 new sites (JFMCs /VFDSs) have been kept for 2019-20. During current year plantation and soil conservation activities will be carried out in all the 31 selected sites by the selected JFMCs/VFDSs as per approved micro plan of each selected JFMCs/ VFDSs.
ii) Vidyarthi Van Mittar Yojna
-
-
- This scheme has been started for the students to sensitize them about the importance of Forests and their role in environmental conservation, to inculcate in students a sense of attachment towards nature conservation, protection of forests and increase forest cover.
- A budget provision of `125.00 lakh has been kept under this scheme during 2019-20 and 150 new schools have to be selected. Till December, 2019, 131.5 hectare area has been selected for raising plantation through 146 schools.
-
iii) Van Samridhi Jan Samridhi Yojna
-
- This scheme has been started to strengthen the NTFP (non timber forest produce) resource base in the state through active community participation. Empowerment of local communities in collection, conservation and marketing of NTFPs to augment the incomes of rural population. The scheme will be implemented initially in 7 most biodiversity rich districts namely, Chamba, Kullu, Mandi ,Shimla, Sirmour, Kinnaur and Lahaul & Spiti and subsequently in the remaining districts of the State.
iv) Ek Buta Beti k Naam (Started during 2019-20)
-
- To sensitize people about the importance of daughters and forest conservation, a new scheme “Ek Buta Beti k Naam” has been launched during 2019-20. It is believed that by planting a sapling in the name of a girl child and with the effort of nurturing each sapling into a tree communities would be sensitized to be more committed towards the rights of the girl-child leading to realization of her full potential. Upon the birth of a girl-child anywhere in the state, the Forest Department would gift robust and healthy tall plants (Saplings) alongwith “kit” & instructions phamplet to the family. The plants will be planted by the parents of the girl during monsoon or winter season as per suitability of the locality either on their homested land or Govt. land.
EXTERNALLY AIDED PROJECTS
Himachal Pradesh Forest Eco-systems Climate Proofing Project (K.F.W assisted)
Himachal Pradesh Forest Eco- systems Climate Proofing Project with the assistance of Germany (KfW) Project is being implemented in Chamba and Kangra districts of the State for the period of 7 years w.e.f. 201516. The cost of the project is `308.45 crore. The Funding pattern of the project is 85.10 percent loan and 14.90 percent State share. The main objective of this project is the rehabilitation, protection and sustainable use of the selected forest eco systems in Himachal Pradesh to increase and secure the resilience of forest eco systems against climate change and ensure flow of forest based products and other services, which benefit the forest dependent communities.
Himachal Pradesh Forest Eco systems Management and Livelihood Improvement Project:
- A new Project namely “Himachal Pradesh Forest Eco systems Management and Livelihood Improvement Project” for 8 years (201819 to 2025-26) amounting to `00 crore has been started with the assistance of Japan International Cooperation Agency (J.I.C.A.).The Funding pattern of the project is 80 percent loan and 20 percent State share. The project will be implemented in Bilaspur, Kullu, Mandi, Shimla, Kinnaur, Lahaul-Spiti districts and tribal areas of Pangi and Bharmour Sub-divisions of Chamba districts with Project headquarter at Kullu (Shamshi), district Kullu and Regional office at Rampur, district Shimla.
- The objectives of the project are to conserve the forest and mountain eco system and improve livelihood of the forest and pasture dependent communities by increasing forest cover, density and productive potential using scientific and modern forest management practices; enhancing biodiversity and forest ecosystem conservation and to reduce pressure/ stress on forest resources by providing the village communities with alternative livelihood opportunity.
World Bank Aided Integrated Development Project for Source Sustainability and Climate Resilient Rain-fed Agriculture:
- The funding pattern of the project is 80 percent loan and 20 percent is State share. The project period is 7 years. The project would be implemented in 900 Gram Panchayats in Shiwalik and Mid Hills agro-climatic zones spread across various watershed in the State. The key objectives of this project include comprehensive treatment of around 2 lakh hectares non-arable and 20,000 hectares arable lands; and enhancement of water productivity/ efficiency Milk production and livelihood improvement in the project area. An outlay of `35.74 crore has been approved under this project during the current financial year 2019-20 out of which expenditure of `7.49 crore has been incurred up to 31.12.2019.
Environment Forestry and Wildlife:
- Himachal Pradesh is home to a very impressive, diverse and unique fauna–many of which are rare.
- The state’s scheme aim at protection, improvement of environment and wildlife, development of wildlife sanctuaries/national parks and improvement of wildlife habitat so as to provide protection to various species of birds and animals facing extinction.
- To protect, develop and scientifically mange the wildlife and to improve its habitat an outlay of `21.25 crore has been approved for the current financial year 2019-20.
| The share of agriculture and allied sectors in the Gross Value Added (GVA) of the State at current prices has declined from 15.35 per cent in 2014-15 to 12.73 per cent in 2019-20 due to relatively higher growth performance of non-agricultural sectors. |

